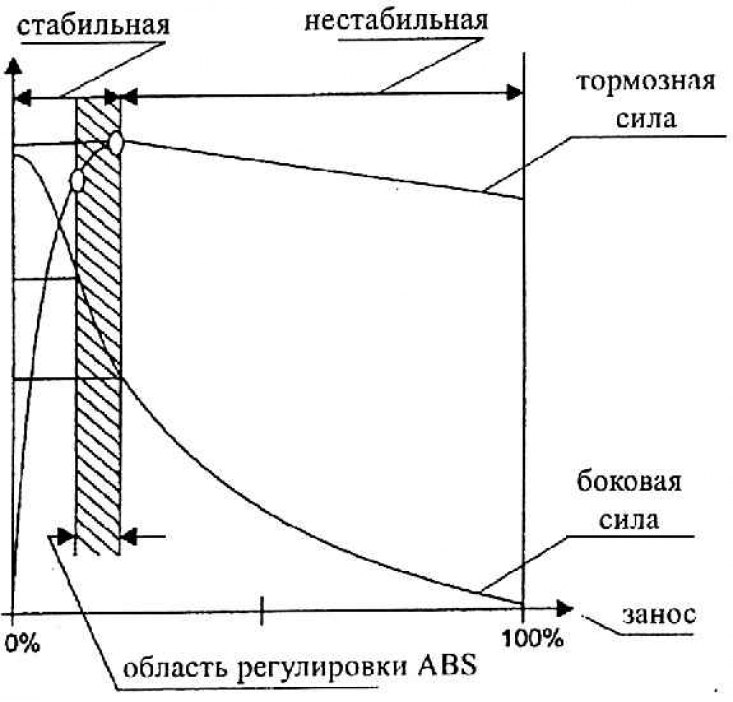
Diagram of lateral force - skid and ABS adjustment area
ABS (anti-block system) is an equipment that contributes to driving safety (during braking). ABS enhances the vehicle's active safety in the following situations: improves the vehicle's handling even under full braking, increases the vehicle's stability, both under full braking and when braking on the road with different adhesion under the right and left wheels, reduces tire wear, as a rule, reduces braking way and thus reduces the physical strain on the driver in critical situations.
The ABS system prevents the wheels from locking under full braking. The principle of its operation is based on the fact that the maximum braking effect is observed at a still rotating wheel. ABS controls the rotation of the wheels and regulates the braking in individual wheels so that the rear wheel does not lock. Interestingly, the ABS principle was patented at the beginning of the last century.
Due to the fact that the wheels rotate even under full braking, there is a sufficiently large force on the front wheels to maintain the controllability of the car. Similarly, at the wheels of the rear axle, when the wheels are rotating, a prerequisite for holding the road is created. (Slip occurs when the rear wheels are locked and cannot transmit any lateral forces.)
