Gasoline engines 1.6 l (AEE) car Skoda Octavia 1
General information about the power unit
The drive unit refers to the engine with the gearbox. On cars of the Skoda Octavia type range, several types of drive units are installed in different combinations of the engine and gearbox. Depending on the...
The drive unit refers to the engine with the gearbox. On cars of the Skoda Octavia type range, several types of drive units are installed in different combinations of the engine and gearbox. Depending on the...
Installation of the drive unit in the body
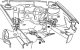
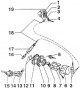
View of the engine compartment with installed elastic pads and a longitudinal support Console on 1.6-55 kW engine (AEE) and its installation on an elastic lining in the body Console on gearbox 02J (CZM, CZL) for landing...
View of the engine compartment with installed elastic pads and a longitudinal support Console on 1.6-55 kW engine (AEE) and its installation on an elastic lining in the body Console on gearbox 02J (CZM, CZL) for landing...
General information about the engine 1.6 l 55 kW (AEE)
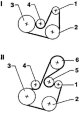
Multi-ribbed motor belt route 1.6–55 kW (AEE) I - car without air conditioning II - car with air conditioning 1 - alternator; 2 - power steering pump; 3 - crankshaft; 4 - tension roller; 5 - guide roller; 6 - air...
Multi-ribbed motor belt route 1.6–55 kW (AEE) I - car without air conditioning II - car with air conditioning 1 - alternator; 2 - power steering pump; 3 - crankshaft; 4 - tension roller; 5 - guide roller; 6 - air...
Main technical data of the engine
Main technical data of the engine Upon reaching 5000 rpm, smooth adjustment of the injector function begins in order to avoid exceeding 6100 rpm.
Main technical data of the engine Upon reaching 5000 rpm, smooth adjustment of the injector function begins in order to avoid exceeding 6100 rpm.
Engine block crankcase (cylinder block) complete
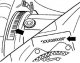
Engine number location The engine number is given together with the engine designation (AEE), embossed on the block under the coolant regulator housing, as well as on the sticker located on the belt drive guard. The...
Engine number location The engine number is given together with the engine designation (AEE), embossed on the block under the coolant regulator housing, as well as on the sticker located on the belt drive guard. The...
Crank mechanism
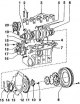
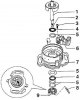
Crankshaft, its location and seal in the crankcase of the engine 1 - bearing shells I, 2, 4, 5; 2 – screws of covers of bearings of the crankshaft; 3 - bearing caps; 4 - insert of the third bearing; 5 - guide rings for...
Crankshaft, its location and seal in the crankcase of the engine 1 - bearing shells I, 2, 4, 5; 2 – screws of covers of bearings of the crankshaft; 3 - bearing caps; 4 - insert of the third bearing; 5 - guide rings for...
Cylinder head and valve-type valve timing mechanism
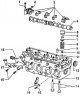
Cylinder head assembly with valve type timing mechanism 1 – a bolt of fastening of covers of the bearing of a cam shaft; 2 – a nut of fastening of covers by the bearing of a cam shaft; 3 - camshaft bearing caps; 4 - cam...
Cylinder head assembly with valve type timing mechanism 1 – a bolt of fastening of covers of the bearing of a cam shaft; 2 – a nut of fastening of covers by the bearing of a cam shaft; 3 - camshaft bearing caps; 4 - cam...
Camshaft — check
The cam shaft is made of steel forging. Valve timing at 1 mm stroke (manufacturer's data):
The cam shaft is made of steel forging. Valve timing at 1 mm stroke (manufacturer's data):
Camshaft drive
Marks for mutual installation of timing gears Timing housings, cylinder head seals and cylinder head cover 1 – a protective casing of a gear belt (top part); 2 - toothed belt; 3 – a bolt of fastening of a pulley of a...
Marks for mutual installation of timing gears Timing housings, cylinder head seals and cylinder head cover 1 – a protective casing of a gear belt (top part); 2 - toothed belt; 3 – a bolt of fastening of a pulley of a...
Cylinder head cover — general information
It is an aluminum alloy casting. A seal is inserted into the groove along the contour of the bearing surface of the cylinder head. In the upper surface of the cover there is a neck for filling engine oil, which is...
It is an aluminum alloy casting. A seal is inserted into the groove along the contour of the bearing surface of the cylinder head. In the upper surface of the cover there is a neck for filling engine oil, which is...
Exhaust manifold (cast iron) — general information
It attaches to the cylinder head on the front side (in the direction of travel). It is mounted on screwed-in studs and tightened with self-locking nuts with a copper-plated surface. A metal-plastic seal is inserted...
It attaches to the cylinder head on the front side (in the direction of travel). It is mounted on screwed-in studs and tightened with self-locking nuts with a copper-plated surface. A metal-plastic seal is inserted...
Inlet piping — design description
Engine accessories 1 - plug of the filler neck; 2 - oil pressure sensor (baroscope); 3 - guide tube of the oil dipstick; 4 - leading part of the oil dipstick tube; 5 - oil dipstick; 6 – a pulley of a belt drive of a cam...
Engine accessories 1 - plug of the filler neck; 2 - oil pressure sensor (baroscope); 3 - guide tube of the oil dipstick; 4 - leading part of the oil dipstick tube; 5 - oil dipstick; 6 – a pulley of a belt drive of a cam...
Fuel injection and ignition control system
Fuel system diagram 1 - a tank with activated carbon; 2 - solenoid valve of the tank with activated carbon; 3 - suction pipeline; 4 - low pressure pipeline; 5 - pressure regulator; 6 - bypass fuel line; 7 - fuel pump; 8...
Fuel system diagram 1 - a tank with activated carbon; 2 - solenoid valve of the tank with activated carbon; 3 - suction pipeline; 4 - low pressure pipeline; 5 - pressure regulator; 6 - bypass fuel line; 7 - fuel pump; 8...
Functional parts of the system 1 AV
Injection control The injection is controlled sequentially. The injection order corresponds to the ignition order. Based on the sensor signals, the duration of the opening of the injection valves is calculated. These...
Injection control The injection is controlled sequentially. The injection order corresponds to the ignition order. Based on the sensor signals, the duration of the opening of the injection valves is calculated. These...
Fuel Tank Ventilation — General
The ventilation system conforms in its design to the most modern engine building standards. The fuel tank communicates with the atmosphere through a tank with activated carbon, which absorbs gasoline vapors. The control...
The ventilation system conforms in its design to the most modern engine building standards. The fuel tank communicates with the atmosphere through a tank with activated carbon, which absorbs gasoline vapors. The control...
Hall sensor — design description
Scheme of sensors and active elements Sensors : 1 - combined intake air pressure sensor (G 70) and its temperature (G 72); 2 - ignition distributor with Hall sensor; 3 - lambda probe (G 39); 4 - knock sensor; 5 -...
Scheme of sensors and active elements Sensors : 1 - combined intake air pressure sensor (G 70) and its temperature (G 72); 2 - ignition distributor with Hall sensor; 3 - lambda probe (G 39); 4 - knock sensor; 5 -...
Temperature sensor (G 72) and incoming air pressure (G 70)
Combined intake air temperature and pressure sensor (inlet pipe mounting) 1 - pressure sensor assembly; 2 – incoming air temperature sensor; 3 - inlet pipeline; 4 - incoming air The combined sensor is mounted directly...
Combined intake air temperature and pressure sensor (inlet pipe mounting) 1 - pressure sensor assembly; 2 – incoming air temperature sensor; 3 - inlet pipeline; 4 - incoming air The combined sensor is mounted directly...
Coolant temperature sensor (G 62)
The coolant temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor and is installed in the thermostat housing. Each temperature of the coolant corresponds to a certain resistance value, transmitted to the control unit in the form of a...
The coolant temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor and is installed in the thermostat housing. Each temperature of the coolant corresponds to a certain resistance value, transmitted to the control unit in the form of a...
Knock sensor
Knock sensor and its placement on the engine block 1 - knock sensor Knock - detonation combustion - CU determines based on the voltage signal from the knock sensor. Knock adjustment is carried out for each cylinder...
Knock sensor and its placement on the engine block 1 - knock sensor Knock - detonation combustion - CU determines based on the voltage signal from the knock sensor. Knock adjustment is carried out for each cylinder...
Lambda control and additional signals
Lambda control in conjunction with a catalyst is the most effective way to reduce the amount of harmful impurities in the exhaust gases of a gasoline engine. The efficiency of the triple-acting catalyst is optimal if...
Lambda control in conjunction with a catalyst is the most effective way to reduce the amount of harmful impurities in the exhaust gases of a gasoline engine. The efficiency of the triple-acting catalyst is optimal if...
Engine control unit — general information
Control unit 1 AV (uu) has two connectors for connecting to the electrical wiring. The connection of the individual elements is shown in the respective wiring diagrams (see subsection 12.5.2 , subsection 12.5.3 ,...
Control unit 1 AV (uu) has two connectors for connecting to the electrical wiring. The connection of the individual elements is shown in the respective wiring diagrams (see subsection 12.5.2 , subsection 12.5.3 ,...
Ignition system — design description
Ignition 1 - ignition module (N 152); 2 - output stage of the high power ignition module - ignition coil (N 157); 3 - resistor (0.6 to 1.4 kOhm); 4 - connector; 5 - three-pole connector of the Hall sensor; 6 - shielding...
Ignition 1 - ignition module (N 152); 2 - output stage of the high power ignition module - ignition coil (N 157); 3 - resistor (0.6 to 1.4 kOhm); 4 - connector; 5 - three-pole connector of the Hall sensor; 6 - shielding...
Ignition distributor and high voltage ignition wires
Distributor (mounting reamer) 1 - the shaft of the ignition distributor with a diaphragm for the Hall sensor; 2 - washer; 3 - 3 Nm; 4 - plastic gasket; 5 - compensation gasket; 6 - Hall sensor (G 40); 7 - distributor...
Distributor (mounting reamer) 1 - the shaft of the ignition distributor with a diaphragm for the Hall sensor; 2 - washer; 3 - 3 Nm; 4 - plastic gasket; 5 - compensation gasket; 6 - Hall sensor (G 40); 7 - distributor...
Spark plugs — general information
For the 1.6-55 kW engine, no other spark plugs can be used, only those approved by the vehicle manufacturer. The most important information about the type of candles is in the Skoda service department. Attention! The...
For the 1.6-55 kW engine, no other spark plugs can be used, only those approved by the vehicle manufacturer. The most important information about the type of candles is in the Skoda service department. Attention! The...
Fuel Injection — Design Description
Nozzle in the suction pipe 1 - nozzle; 2 – a head of the block of cylinders; 3 - suction channel in the block head; 4 - suction channel in the pipeline; 5 - fuel injection Throttle control unit 1 - sliding contact; 2 -...
Nozzle in the suction pipe 1 - nozzle; 2 – a head of the block of cylinders; 3 - suction channel in the block head; 4 - suction channel in the pipeline; 5 - fuel injection Throttle control unit 1 - sliding contact; 2 -...
Disconnecting the fuel injection in exceptional cases
Engine braking During engine braking, the fuel supply will be disconnected even before the programmed engine speed is reached under the following conditions: throttle valve closed; the coolant temperature is within the...
Engine braking During engine braking, the fuel supply will be disconnected even before the programmed engine speed is reached under the following conditions: throttle valve closed; the coolant temperature is within the...
Electrical connection of the injector relay and fuel pump
The injectors are permanently connected through the fuel pump relay and are controlled from the control unit grounded to the housing. The electrical connection of the injector relay and the fuel pump is shown in the...
The injectors are permanently connected through the fuel pump relay and are controlled from the control unit grounded to the housing. The electrical connection of the injector relay and the fuel pump is shown in the...
Own diagnostics of the ignition system
The task of self-diagnosis is primarily to identify defects in the operation of the MPI system. While the engine control is working, the control unit constantly monitors this work, as well as the correctness of the...
The task of self-diagnosis is primarily to identify defects in the operation of the MPI system. While the engine control is working, the control unit constantly monitors this work, as well as the correctness of the...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Link to this section in various formats
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- User manual
- Car driving
- Maintenance
- Petrol engines 1.2 l
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Petrol engines 1.4 l
- Engine repair
- Supply system
- Petrol engines 1.8/2.0 l
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Diesel engines 1.6/2.0 l
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Transmission
- Mechanical gearbox 02S
- Automatic gearbox 0CW
- Automatic gearbox 0D9
- Chassis (running gear)
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Steering
- Body and interior
- Doors, locks and windows
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Ventilation and air conditioning
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Headlights and lighting
- Wiring diagrams (basic)
- Wiring diagrams (comfort)
- General information
- Vehicle details
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines 1.6 l AEE
- Petrol engines 1.8 l AGN
- Diesel engines 1.9 l AGR
- Fuel system
- Exhaust system
- Cooling system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Gearbox repair 02J
- Gearbox repair 02K
- Chassis (running gear)
- Wheels and tires
- Suspension and axles
- Brake system
- Body and interior
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits