Nozzle in the suction pipe
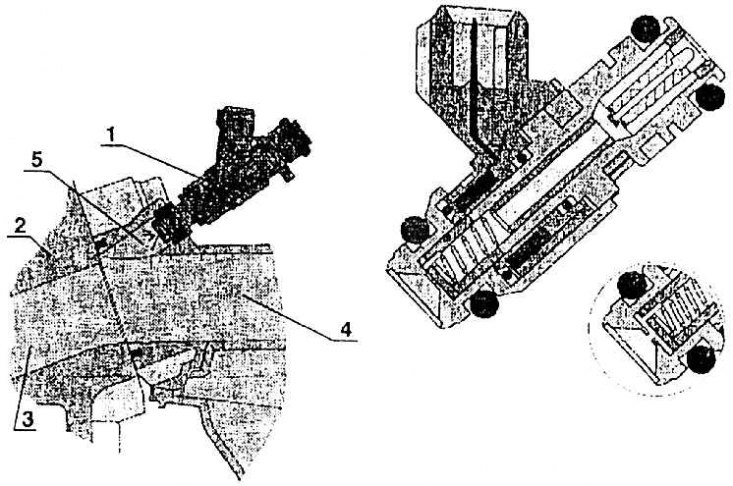
1 - nozzle; 2 – a head of the block of cylinders; 3 - suction channel in the block head; 4 - suction channel in the pipeline; 5 - fuel injection
Throttle control unit
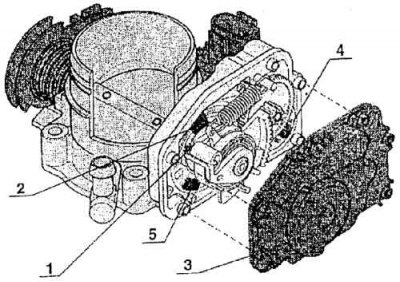
1 - sliding contact; 2 - throttle potentiometer; 3 - casing of the node; 4 - throttle control motor; 5 – setpoint potentiometer
Difference between the special shape of the suction inlet of the 1.6–55 kW motor and the 1.8–92 kW motor and the cylindrical shape
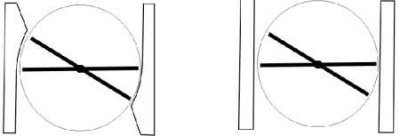
drawing on the left: special shape (spherical surface - calot);
drawing on the right: cylindrical shape
Fuel injection is an integral part of the MPI system and consists of:
- injection distributor strips with nozzles;
- pressure regulator;
- throttle control assembly.
Injection distributor bar
The injection distributor rail forms a mounting kit with the injectors installed on the suction pipe. The nozzles are placed on the bar in a row and sealed on the suction pipe with rubber washers. When installing the intake pipe on the cylinder head, make sure that neither the seal nor the seating surface is damaged. The tightening torque of all eight fixing bolts must be the same (M - 20 Nm). The nozzles are controlled by pulses using electromagnets of the control unit. Fuel is injected into the intake port and, together with air, enters the combustion chamber of the corresponding cylinder (see fig. Nozzle in the suction pipe).
Fuel pressure control
A fuel pressure regulator is installed on the left side of the distributor bar. The regulator maintains a constant difference between the pressure in the suction pipe and the fuel pressure. Thus, a change in the pressure in the suction pipe does not affect the amount of injected fuel. When the engine is off, the regulator blocks the flow of fuel back into the tank and thereby maintains fuel pressure in the system. The pressure regulator is installed during pre-assembly and its parameters cannot be changed.
Throttle control unit
Node task (see fig. Throttle control unit) is the stabilization of the engine idling in various conditions and under different loads. The adjustment is carried out by the CU. The sliding contact, the throttle valve potentiometer and the throttle valve adjuster potentiometer inform the control unit about changes in the position of the throttle valve and the ignition distributor.
To adjust the throttle valve at idle, a throttle valve control controlled from the control unit is used.
The idle control unit must not be opened and mechanically interfered with its adjustment. Installation can only be done in the Skoda service using the VAG 1552 tester.
The air flow in the throttle valve is shown in fig. Difference between the special shape of the suction inlet of the 1.6–55 kW engine and the 1.8–92 kW engine and the cylindrical shape. The special shape of the suction neck allows for the finest adjustment of the amount of air at idle, as well as a very fine response to the gas pedal.
