Exhaust Assembly - 1.8-92 kW Engine
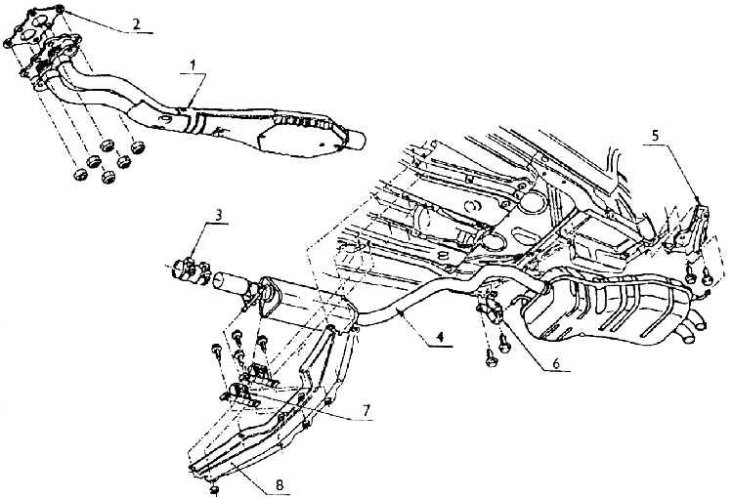
1 - the front of the exhaust with a catalyst; 2 - seal; 3 - clamp; 4 – a back part of an exhaust; 5 - rear bracket; 6 - middle bracket; 7 - front bracket; 8 - bearing structure of the exhaust
On vehicles with 1.8–92 kW engines, the exhaust path consists of two parts. The front part of the exhaust is attached to the manifold flange with a 10 mm thick flange with six bolted connections.
A metal seal is inserted between the flanges, made of three connected thin steel sheets with an extruded sealing profile around the round holes.
The seal must be replaced with a new one each time it is dismantled.
If the manifold flange has two outlets, the connected exhaust front also has two pipes. They are then combined into one and a controlled catalyst, relatively large and long, is welded to it.
The oscillation of the engine in relation to the exhaust pipe allows the elastic element under the flange. The gap existing between the outlets from the flange and the connected branches of the pipeline is covered by two bellows welded to both flanges. On the sides between the flanges are so-called vibration dampers.
The dampers consist of pins with lenticular plates welded to the top flange and inserted into cylindrical housings, which in turn are welded to the bottom flange. The voids are filled with steel fibers. The design solution allows vibrations, but prevents damage to the bellows in case of separation of the entire lower part of the pipeline.
A holder for an oxygen probe is placed in the oncoming flow cone at the front of the catalyst. The catalyst itself is trimetallic (platinum, palladium and rhodium). A heat shield is welded to the bottom of the catalyst, which protects the chassis from heat radiation. There is also a heat shield above the entire exhaust system under the floor.
The front pipe at the rear of the exhaust is connected to the pipe leaving the catalytic converter with a two-piece clamp with fasteners that provides a good seal.
The position of the clamp is set by marks on both parts, and there is also a certain gap between the ends of the tubes. An expansion chamber is located behind the clamp.
In front of the expansion chamber, a bracket is welded onto the pipeline with two fingers inserted into a rubber-metal socket screwed to the cross member and thus to the body.
The exhaust ends in a powerful, volume-moulded muffler, from which two end tubes exit, bent by the outlet ends to the chassis.
In front of the muffler and behind it there is one elastic suspension, for which the muffler, or the rear part of the exhaust is attached. Consequently, all exhaust in vehicles with 1.8–92 kW engines is suspended on three hangers.
Neither the entire exhaust nor any of its parts may be replaced by an exhaust of a different design. Individual parts can also be replaced independently, but only for parts of the same order number.
