Location of fuel tank accessories in vehicles with 1.9 TDI engine
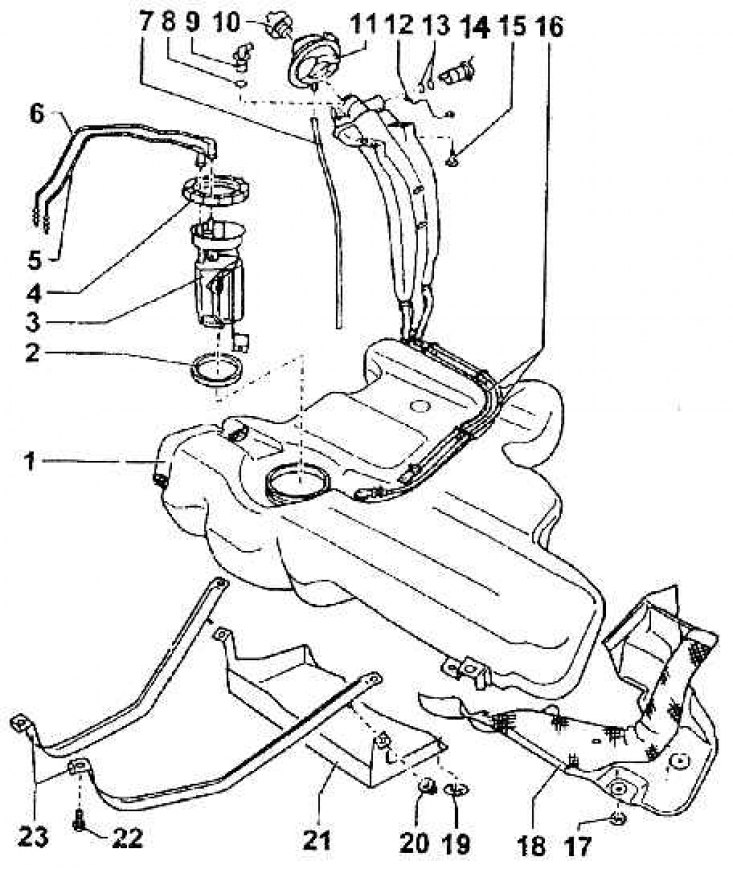
1 - fuel tank; 2 - sealing washer; 3 - fuel level sensor in the tank; 4 - union nut (M = 80 Nm); 5 - fuel line - supply to the engine (painted black); 6 - return fuel line; 7 - air outlet hose; 8 - washer; 9 - combined valve; 10 - neck plug; 11 - elastic washer; 12 - grounding on the body; 13 - washer; 14 - air outlet valve; 15 - ground wire terminal bolt; 16 - air outlet pipeline; 17 - mounting gasket; 18 - heat-insulating damper - sheet; 19 - mounting gasket; 20 - nut; 21 - casing; 22 - fastening strip bolt (M = 25 Nm); 23 - belts supporting the tank
Fuel tank with accessories (engine 1.8 - 92 kW)
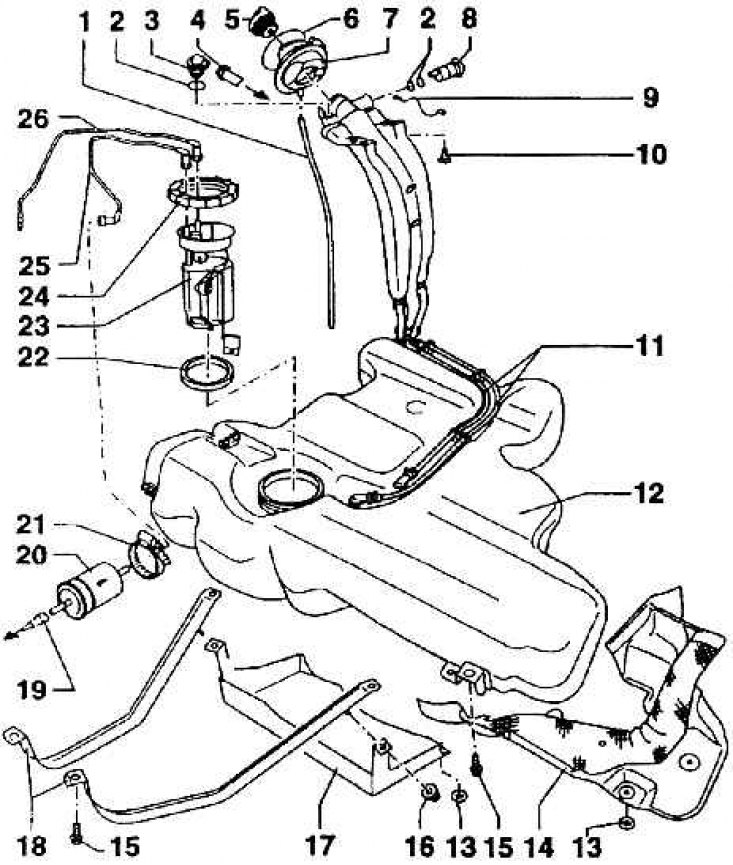
1 - hose for supplying air to the tank; 2 - sealing washer; 3 - combined valve; 4 - air outlet pipeline (to the activated charcoal tank); 5 – a stopper of a fuel tank; 6 - elastic washer; 7 - rubber seal; 8 - air outlet valve; 9 - grounding to the body; 10 - ground terminal bolt; 11 - air outlet tube; 12 – fuel tank; 13 - mounting gasket; 14 - thermal insulation protection; 15 – protection fastening bolt; 16 - nut; 17 - casing; 18 - fastening belts; 19 - fuel line (to the engine); 20 - fuel filter; 21 – a clamp of fastening of the fuel filter; 22 - sealing washer; 23 - fuel pump; 24 - union nut; 25 - fuel line to the fuel filter; 26 - fuel line for reverse overflow of fuel from the engine
Fuel tank - diagram
1 - plug of the filler neck; 2 - an insert that limits the use of the mouthpiece of a fuel gun for gasoline with lead; 3 - insert in the neck of the tank for diesel fuel; 4 - air outlet tube; 5 - fuel return overflow line; 6 - fuel line to the engine; 7 - belts for attaching the tank; 8 - combined valve
Pipeline for venting air from the filler neck
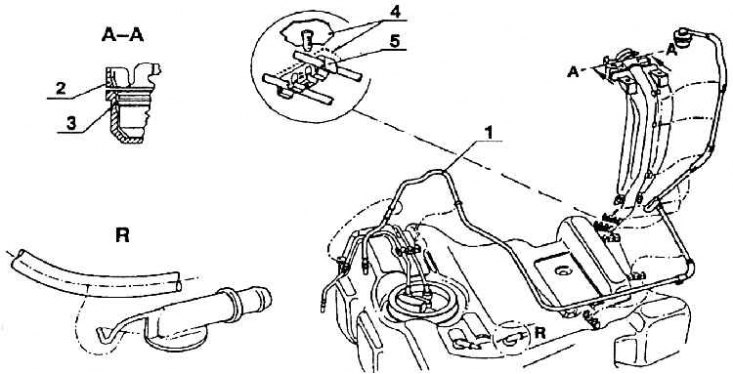
1 - air outlet pipeline; 2 – flange with gravity valve; 3 - seal; 4 - floor sheet; 5 - pipeline bracket
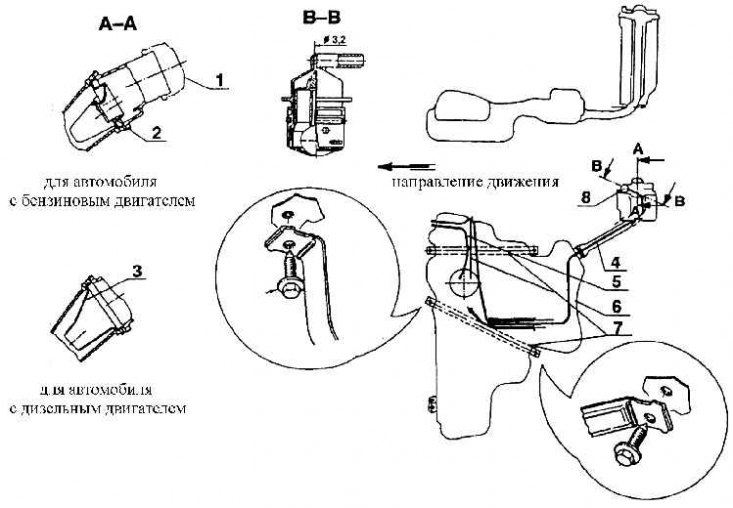
Installing the fuel pump in the tank (vehicles with petrol engines)
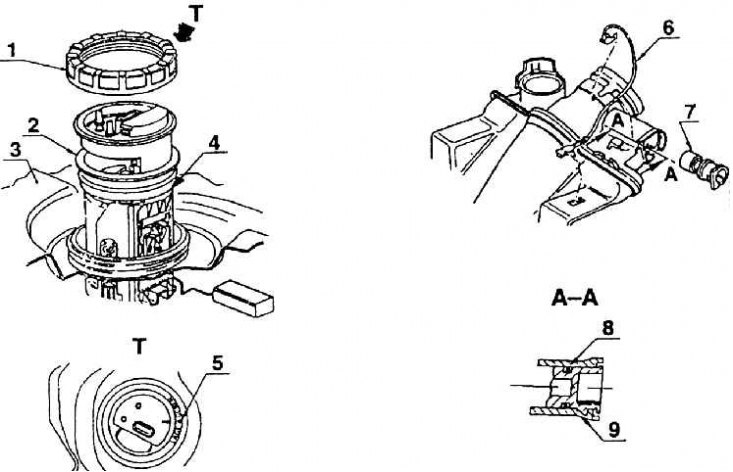
1 - union nut; 2 - seal; 3 - fuel tank; 4 fuel pump; 5 - mounting designation;
Details of a mouth of a fuel tank: 6 – grounding; 7 - valve for air removal; 8 - seal; 9 - installation of a valve for venting air
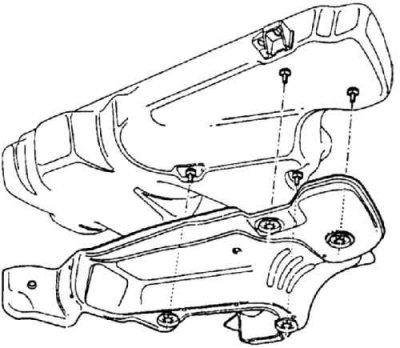
Fuel tank heat shield
Although the fuel tank is part of the bodywork, it must be classified thematically as part of the fuel system and is therefore included in the Fuel System chapter.
Fuel tank made of plastic (polyethylene TL 669) black color. The manufacturing technology provides the possibility of its molding with the maximum possibility of using the space intended for it. It is located under the rear seats, under the floor in the so-called safety zone. The plastic from which the tank is made does not allow the formation of an electric charge, which is common when using ordinary plastic, therefore, from this point of view, the tank is completely safe. The volume of the tank is approximately 55 liters.
Fuel tanks for gasoline vehicles are conceptually the same as those for diesel vehicles. They differ only in the liners in the filler neck and in the fact that an electric fuel pump, combined with a level gauge, is built into the fuel tank designed for cars with a gasoline engine. The tank, designed for vehicles with a diesel engine, has only a suction system and a level gauge (the pump is in the fuel injection system).
The fuel tank assembly also includes the fuel filler assembly, bleed hose system, and fuel hose.
Electric fuel pump (in the petrol tank), as well as a suction system with a level gauge (in diesel tank) are inserted through a wide opening under a mouth in the top surface of a tank. Both are attached with the same plastic union nut. There are two fittings for fuel hoses in the cover. Fuel is supplied to the engine through one hose, and excess fuel is returned through the other. On the cover and the neck of the tank there is a designation for installation. The cover also contains a connector for connecting wiring to the level gauge.
The filler neck of the fuel tank has a separate grounding to the body, which protects against electrical breakdown when filling the tank. There is also an insert in the neck. In a gasoline tank, the liner prevents the mouthpiece of a fuel gun designed for gasoline with lead from being put on; in the diesel fuel tank, a funnel-shaped liner prevents fuel from splashing out when filling the tank. There is also a combined gravity valve in the filler neck, which allows air to be vented, but closes when the car is turned over and thus prevents fuel from escaping. The valve cross section at the outlet is reduced (diameter 3.2mm) to prevent accidental flame penetration. There is also an air vent valve in the neck, which is closed during the filling of the tank and opens mechanically when the cork is placed on the neck. The valve prevents the tank from overfilling when refueling.
As long as the filler cap is fitted with a patented lock (in some versions of cars), which can be opened with a key common to door locks and the ignition lock, the key is designed in such a way that the key made for the insert in the plug cannot be used in door and ignition locks. This prevents the car from being stolen by a key made for the lock insert of the stolen filler cap.
The tank is fixed in the body cavity with two belts, then with grippers (bolts M 8) in the left front of the tank and two M6 bolts holding the filler neck at the right rear fender liner. After unscrewing the mentioned connections, the tank can be removed. Its installation is done in the reverse order.
At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that none of the hoses is pressed, not only because of the easier filling of the tank, but also because of the air supply when pumping fuel while driving. If air is not supplied to the tank, it may deform when fuel is pumped out.
An integral part of the tank is a casing, which also serves as thermal insulation from the exhaust.
