Mounting reamer of the clutch (the trip rod is led through the gearbox shaft)
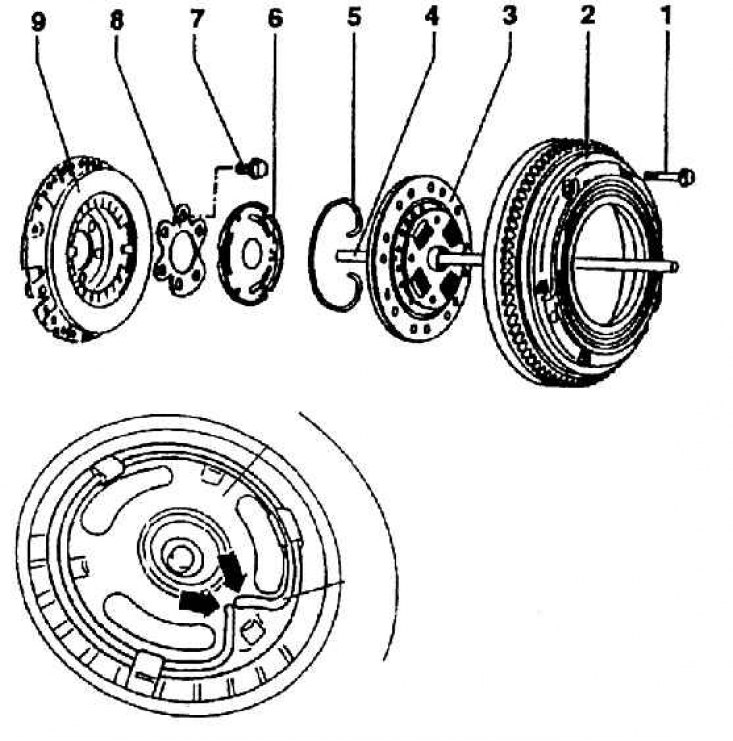
1 – a bolt of fastening of a flywheel; 2 - flywheel; 3 - friction disc (plate); 4 - disconnecting the clutch; 5 - clamping ring; 6 - disconnecting plate; 7 – a bolt of fastening of a pressure disk to a cranked shaft; 8 - overlay; 9 - clutch pressure plate
Clutch release mechanism used in 02K gearboxes (AEE motors 1.6–55 kW)
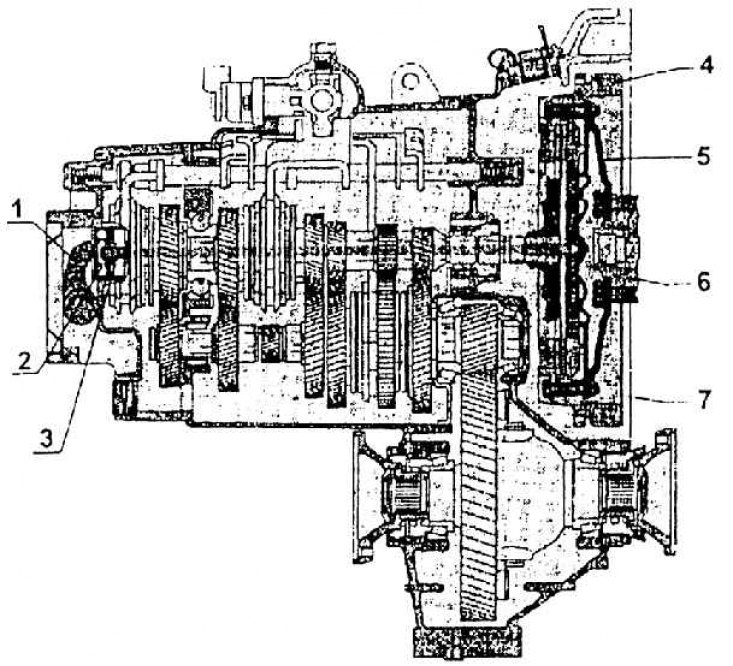
1 – clutch lever; 2 - disabling thrust bearing; 3 - disabling push rod clutch; 4 - flywheel; 5 - clutch pressure plate; 6 - crankshaft; 7 - gearbox housing
Mounting reamer of hydraulic clutch release (clutch with breaking rod passed through the gearbox shaft)
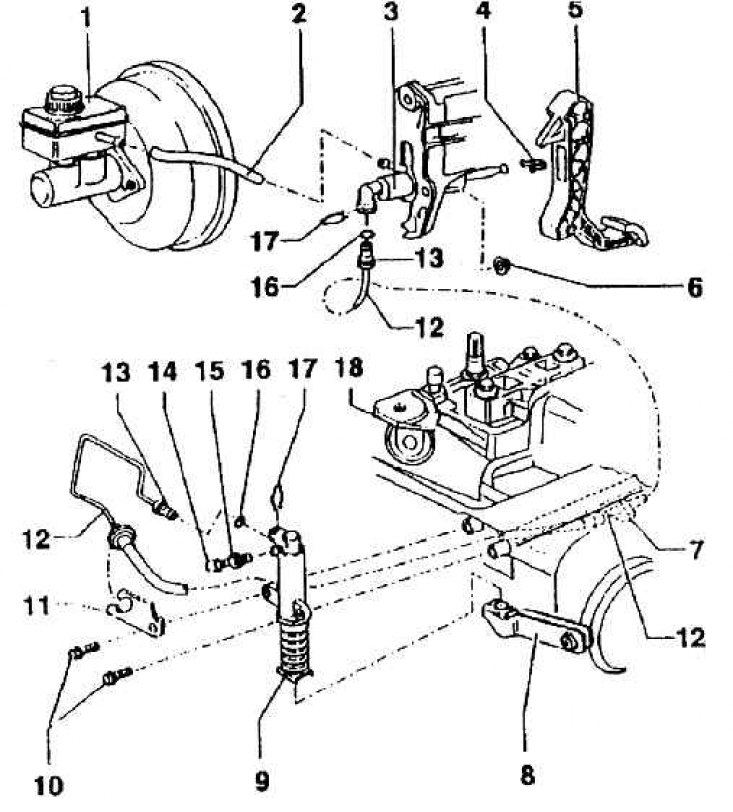
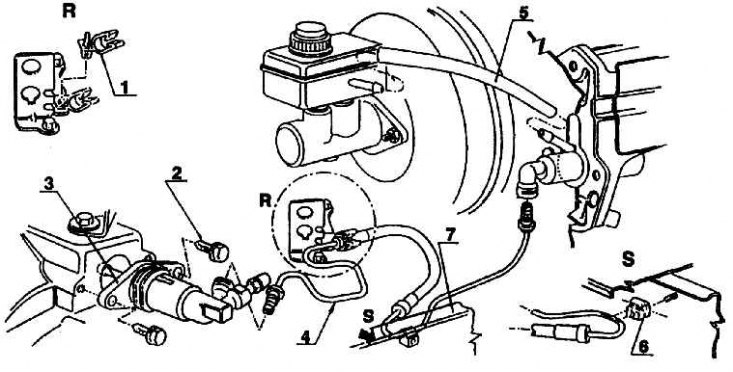
1 - spare brake fluid tank; 2 - hose; 3 - hydraulic clutch release cylinder; 4 - support; 5 - clutch pedal; 6 - self-locking nut (M = 25 Nm); 7 - bracket; 8 – clutch lever; 9 - pressure hydraulic cylinder; 10 – a bolt of fastening of the pressure cylinder; 11 - bracket; 12 - pressure pipeline; 13 - tip of the pipeline; 14 - cap; 15 - deaeration valve; 16 - sealing washer; 17 - safety bracket; 18 - gearbox
Diagram of the clutch release mechanism used in the 02J gearbox in conjunction with AGN 1.8-92 kW engines (CZM gearbox) and AGR 1.9 TDI - 66 kW (CZL gearbox)
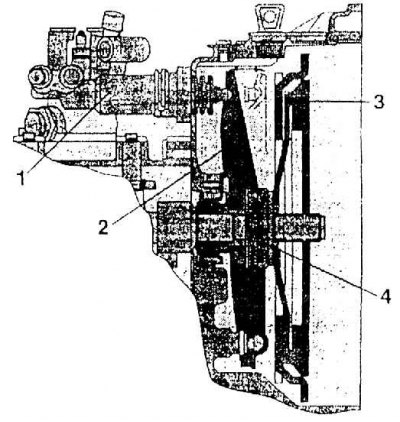
1 – working hydraulic clutch cylinder; 2 – disconnecting clutch lever; 3 - clutch; 4 - disabling clutch bearing
Hydraulically actuated clutch release mechanism with classic lever and bearing release arrangement
1 - hose holder; 2 - bolt; 3 – working hydraulic cylinder; 4 - pipeline; 5 - hose; 6 - bracket; 7 - spar
In Skoda cars of the Octavia type range with a manual gearbox, a dry clutch is installed, single-disk with a poppet (membrane) spring.
For clutch discs (plates) friction surface without asbestos, they have axial suspension in the space between the friction surfaces. All inserts also have a snag damper (four helical springs in the metal part of the disc) and a pre-damper that eliminates vibration due to structural gaps in the transmission (gaps between the teeth in the gearbox) at idle. Based on the installed engine, a clutch with a different diameter of the friction disc is selected, and based on the type of gearbox, their disengagement mechanisms also differ.
Engine 1.6-55 kW, to which a gearbox type 02K is attached (CZE), has a clutch with a friction layer outer/inner diameter = 200/143 mm and a trip rod passing through the transmission drive shaft.
1.8 - 92 kW engine coupled with type 02J mechanically controlled gearbox (CZM), has a clutch with outer / inner diameter of the friction layer 216 / 155 mm and a classic cut-off.
1.9 TDI engine - 66 kW to which type 02J gearbox is attached (CZL), has a similar grip to the classic cut-off type. The outer and inner diameter of the friction layer of this clutch is 228/150 mm.
The transmission of force and movement between the clutch pedal and the disengagement mechanism in both types of clutch is carried out by a hydraulic transmission, naturally differing in design.
The clutch, designed to be connected to the 02K gearbox, has an arrangement used on Skoda cars for the first time. Its advantage is the possibility of reducing the drive unit and the use of a tripping mechanism without a thrust tripping bearing. Shutdown travel 5.5±1 mm.
The pressure plate is mounted on the crankshaft flange and on its belleville spring (with shortened landing elements) presses the pressure plate, clamped by an elastic wire safety ring. friction disc (plate) is laid between the friction surface of the pressure plate and the friction surface of the flywheel. The flywheel is screwed along the outer contour into the pressure plate flange. The friction disc is seated with its splined hub on the splined shaft of the gearbox. Through this same shaft, the control rod for disengaging the clutch passes along the axis, based on the pressure element. The clutch kit is shown in fig. Mounting reamer of the clutch (the trip rod is led through the gearbox shaft), sectional view - in fig.
Clutch release mechanism used in 02K gearboxes (AEE motors 1.6–55 kW).
Clutch release mechanism (see fig. Mounting reamer of hydraulic clutch release (clutch with breaking rod passed through the gearbox shaft)) transfers force and movement from the clutch pedal to the already mentioned release control rod by means of two hydraulic cylinders. One of them is mounted on the pedal console, the second - on the gearbox.
The working fluid is the brake fluid coming from the reserve tank of the main brake tandem cylinder. After changing the brake fluid, the system must be bled of air. A hydraulic cylinder on the gearbox presses the release rod by means of a linkage.
Clutch designed to be connected to gearbox type 02J for 1.8-92kW and 1.9 TDI-66kW engines. The clutch for both types of engines has the same concept and a similar design solution, the difference is only in the diameters of the friction layer of the plate. Classic clutch design. A flywheel is screwed onto the crankshaft flange, and a pressure plate is attached to it. A friction disc is placed between the friction surfaces of both mentioned parts (plate). To poppet (membrane) The pressure plate spring is supported by a thrust bearing in a grease-lubricated plastic bushing.
When the clutch is disengaged, the bearing is pressed by a lever fixed so that it can rotate inside the clutch housing. The lever is operated by a piston rod of a working hydraulic cylinder located outside the clutch housing. When the friction layer wears out, the clutch mechanism adjusts automatically. Trip travel 8±1 mm (see fig. Diagram of the clutch release mechanism used in the 02J gearbox in conjunction with AGN 1.8-92 kW engines (CZM gearbox) and AGR 1.9 TDI - 66 kW (CZL gearbox)).
The disengaging mechanism is controlled from the clutch pedal by a hydraulic transmission - two hydraulic cylinders connected by a pipeline. Brake fluid comes from the reserve tank of the brake system. After changing the brake fluid, the system must also be deaerated. The hydraulic drive system is shown in fig. Hydraulically actuated clutch release mechanism with classic lever and bearing release arrangement.
