Note. Below is a description of possible faults for all turbochargers. This is a general description, so some problems may not be specific to your engine.
If you experience engine performance problems—loss of power, poor throttle response, abnormal engine noise, or engine oil leaks—the troubleshooting procedures should be followed:
1. Check the correctness and reliability of the assembly and connection of the turbocharger to the exhaust pipe.
- A. Check and make sure new gaskets are installed.
- B. Check and make sure that the fastening bolts and nuts are securely tightened
- C. Check connections for exhaust gas leaks.
- D. Check all elements of the intake and exhaust system for damage and breakage.
Exhaust gas leaks due to a damaged or not installed gasket, as well as bolts not properly tightened (or nuts) fasteners can lead to abnormal sounds in the engine.
If these malfunctions are detected, it is necessary to unscrew and tighten the fastening bolts and nuts with the required tightening torque. If necessary, replace a damaged gasket.
2. Check the correctness and reliability of the assembly of the turbocharger with the exhaust manifold.
- A. Check and verify that the gasket is installed between the turbocharger and the manifold.
- B. Check and verify that the mounting bolts and nuts are secure.
- C. Check connections for exhaust gas leaks.
- D. Check all elements of the intake and exhaust system for damage and breakage.
Exhaust gas leaks due to a damaged or not installed gasket, as well as bolts not properly tightened (or nuts) fasteners can lead to abnormal sounds in the engine.
If these malfunctions are detected, it is necessary to unscrew and tighten the fastening bolts and nuts with the required tightening torque. If necessary, replace a damaged gasket.
3. To check up correctness and reliability of installation of a final collector on a head of the block of cylinders.
- A. Check and verify that a new gasket is installed between the manifold and the cylinder head.
- B. Check and verify that the mounting bolts and/or nuts are secure.
- C. Check connections for exhaust gas leaks.
Exhaust gas leaks due to a damaged or not installed gasket, as well as bolts not properly tightened (or nuts) fasteners can lead to abnormal sounds in the engine
If these malfunctions are detected, it is necessary to unscrew and tighten the fastening bolts and nuts with the required tightening torque. If necessary, replace a damaged gasket.
4. Check the reliability and correctness of the connection to the turbocharger and to the engine of the inlet and return oil pipe.
- A. Check and verify that new nozzle gaskets are installed.
- B. Check and verify that the mounting bolts and/or nuts are secure.
- C. Check oil pipes for damage (excessive bending, twisting or cracking).
Exhaust gas leaks from a damaged or misplaced gasket, or improperly tightened mounting bolts, can lead to engine oil leaks.
If the inlet pipe is damaged, there may be a lack of oil injected into the center housing of the turbocharger, this can lead to its damage. If the return pipe is blocked or clogged, the process of draining oil from the turbocharger is disrupted, which can lead to engine oil leaks.
If these malfunctions are detected, it is necessary to unscrew and tighten all the bolts (or nuts) fasteners with the required tightening torque. Replace nozzle gaskets or nozzles. if necessary.
5. Check for engine oil leaks at the connection of the center housing to the compressor housing.
- A. Check and verify the reliability of the fasteners.
- B. Check for engine oil leaks.
Damaged O-ring can cause engine oil leaks (gaskets) between the center housing and the compressor housing.
If engine oil leaks are found, the turbocharger assembly must be replaced
6. Check the vacuum hose of the actuator, as well as the hoses and pipes of the turbocharger.
- A. Verify that the vacuum hose is correctly and securely connected to the turbocharger actuator.
- B. Check and make sure that the vacuum hoses and fittings are not defeated (excessively bent, twisted, or torn).
- C. Check the vacuum pipes for cracks.
- D. Check and verify that the vacuum hoses are properly connected to the outlet and inlet on the solenoid valve.
Loss of power and poor response to the accelerator pedal may result from damaged or disconnected vacuum hoses and fittings.
If this malfunction is detected, it is necessary to replace all damaged nozzles.
7. Check the operation of the turbocharger actuator.
A. Electronic actuator (depending on configuration): check and make sure that the stem moves smoothly and without sticking when a control signal is applied to the actuator, using special equipment.
Note. In the figure below, the turbocharger is shown schematically, therefore it may differ from the real one.
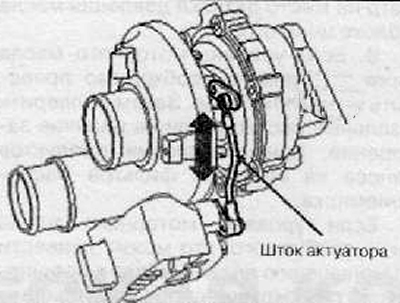
Loss of engine power and poor response to the accelerator pedal can cause damage to the turbocharger actuator.
If this defect is found, the turbocharger assembly must be replaced.
8. Check compressor impeller.
- A. Check the compressor impeller for damage to the blades, as shown in the figure below
- B. Check the smoothness of rotation of the compressor.
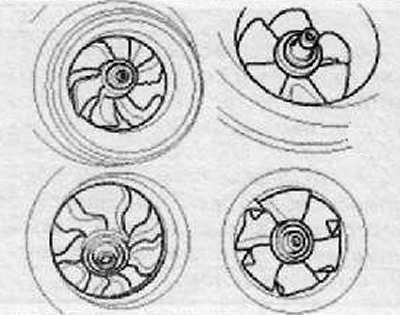
The reason for the abnormal sound of the engine and a weak reaction to the accelerator pedal may be damage to the compressor impeller.
If any defects associated with the compressor impeller are found, the turbocharger assembly must be replaced.
9. Check the technical condition of the turbine impeller.
- A. Check the turbine impeller for damage to the blades as shown in the figure below.
- B. Check the smooth rotation of the turbine.
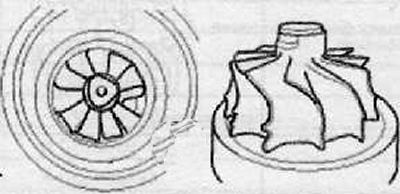
The reason for the abnormal sound of the engine and a weak reaction to the accelerator pedal may be damage to the turbine impeller.
If any defects associated with the turbine impeller are found, the turbocharger assembly must be replaced.
If the cause of engine malfunctions is not directly related to the turbocharger, it is necessary to check all systems related to boost.
1. Check the pressure relief hose.
- A. Check the ventilation hose for damage or improper installation.
- B. Check the valve of the forced crankcase ventilation system (PCV) for contamination.
If the vent hose is damaged or clogged, internal pressure in the engine may increase, which will lead to poor engine oil supply to the turbocharger and subsequent failure and / or oil leaks.
If these defects are found, it is necessary to replace the ventilation hose or system elements.
2. Check the reliability of the connection of the air pipe with the turbocharger.
- A. Check the technical condition of the air pipe (for damage, cracks or crushing).
If the air inlet is reduced in size due to damage, kinking, or excessive bending, the intake air pressure will drop sharply. This may result in turbocharger failure or engine oil leaks. If the air pipe is torn or disconnected, foreign objects can get into the turbocharger, causing it to fail.
If any defects are found in the air pipe, it must be replaced with a new one.
3. Check the air filter.
- A. Check filter element.
- B. Check the air filter for water in the housing.
- C. Check air filter cover for dirt.
- D. Check and verify that the filter element part number is correct.
If the air filter is clogged, the intake air pressure will drop sharply. This can result in turbocharger failure or engine oil leaks.
If any abnormalities are found in the operation of the turbocharger, it is necessary to replace the air filter with a new one.
4. To check a technical condition of hoses and branch pipes of an intercooler.
- A. Check and verify that the intercooler hoses and fittings are properly and securely connected.
- B. Check intercooler pipes and hoses for damage (excessive twisting, bending or tearing).
- C. Check intercooler pipes for cracks (depending on configuration).
- D. Check and make sure that all mounting clamps are properly positioned.
If the pipes or hoses of the intercooler are damaged or disconnected, engine oil may leak through the hoses and pipes, as well as an increase in the maximum permissible speed of the turbocharger with its subsequent failure.
If any defects are found in the pipes and hoses of the intercooler, they must be replaced with new ones.
Note. When replacing pipes and hoses of the intercooler, it is necessary to replace their clamps and their fastenings.
5. Check the technical condition of the intercooler.
- A. Check coolant pipes and reservoirs for damage.
If the intercooler is damaged, it is possible to increase the maximum permissible speed of the turbocharger with its subsequent failure.
If any defects are found in the intercooler, it must be replaced with a new one.
Note. When replacing the intercooler, the hose and pipe clamps must be replaced.
6. Check the technical condition of the engine oil.
- A. Check engine oil level.
- B. Check engine oil for discoloration, water intrusion and loss of viscosity.
- C. Check engine oil for recommended standards.
If the engine oil level is below the required level, this may result in reduced oil supply to the turbocharger bearings and poor heat dissipation.
If this violation is detected, it is necessary to add engine oil to the required level or replace it.
Note. Check the oil for compliance with the required characteristics.
7. Check the engine oil pressure in the engine system.
- A. Measure the engine oil pressure in the system by installing a pressure gauge in place of the oil pressure sensor in the cylinder block.
- B. If the engine oil level is below the required level, check the oil receiver. Then check the oil nozzles for clogging, with the accumulation of wear products on the oil receiver strainer.
If the engine oil level is below the required level, this may result in reduced oil supply to the turbocharger bearings and poor heat dissipation.
Upon detection of this violation. it is necessary to add engine oil to the required level or replace it. With the accumulation of wear products, it is necessary to wash and clean the oil receiver mesh filter, it is also necessary to replace the gaskets of the oil sprayers, having previously checked the cleanliness of the sprayer channels. Check the technical condition of all elements of the lubrication system, e.g. oil pump (see chapter «Lubrication system»),
Attention. Always pay special attention to the quality and condition of the engine oil, as the loss of its viscosity and other characteristics can lead to serious damage to the turbocharger, which rotates at a speed of 100 thousand rpm. Also pay attention to the entire lubrication system as a whole.
8. Check the technical condition of the turbocharger solenoid valve.
- A. Check and make sure that there is a vacuum in the vacuum hose of the actuator when switching the turbine operating mode using special diagnostic equipment (checking the operation of the solenoid valve).
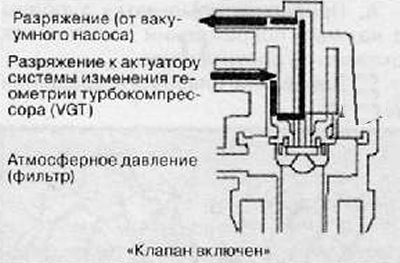
- B. When changing the operating mode of the turbine (using special diagnostic equipment) to forced - the vacuum in the vacuum hose of the actuator should be quickly reset. If the filter of the solenoid valve is clogged, then the vacuum will either not be reset, or will decrease very slowly.
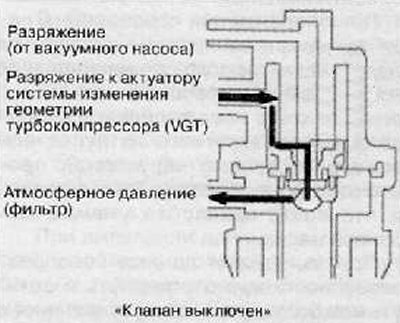
If the solenoid valve is damaged, the VGT system actuator will not work properly, resulting in a loss of engine power and poor response to the accelerator pedal. If the solenoid valve filter is clogged, the turbocharger assembly may fail due to excessive speed.
If defects are found in the solenoid valve, it must be replaced with a new one.
9. Check the technical condition of the fuel injectors, sensors, exhaust gas recirculation valve, etc.
- A. Check the operation of the fuel injectors.
- B. Check the technical condition of the sensors of the engine management system, such as the mass air flow sensor (MAPS), intake air temperature sensor (IATS) and charge air pressure sensor (BPS).
- C. Check and verify that the EGR valve (EGR) works properly.
Violations in the operation of fuel injectors, sensors, exhaust gas recirculation valve (EGR) etc. may result in a loss of vehicle power.
If any malfunctions or defects are found, it is necessary to replace the damaged elements with new ones.
