The DSG code is on the vehicle data sticker (see Introduction). In addition, identification data is also indicated on the DSG itself at the top and bottom (see illustration 1.1): Here "PRC" - DSG code, "15.01.08" - date of manufacture (January 15, 2008), "14" - factory code, "09:49" - production time, and "0042" - serial number.
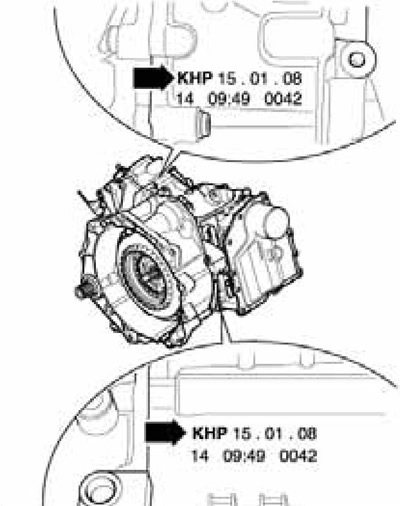
1.1 Location of DSG identification data "OAM"
The main feature of the DSG is the presence of two parallel clutches, which allows two gears to be selected at once (only one gear included). Therefore, when shifting gears, time is spent only disengaging one clutch and engaging the other. Clutch shift points overlap during gear shifts, allowing acceleration with virtually no interruption in power flow, saving between 4 and 8% fuel. Interruption in power flow is a major disadvantage of traditional manual transmissions, automatic transmissions and manual CVTs.
DSG transmission "OAM" is an improved version of the 6-speed DSG 02E transmission (see Part B). It uses two single-disk dry clutches. The kinematic scheme is shown in illustration 1.2. Torque from the engine is transmitted to the dual clutch via a 2-mass flywheel. As in a manual transmission, gear ratios are formed by pairs of gears located on two input and three output shafts. All gears are cylindrical helical. Because two clutches are used, the input shaft is divided into two coaxial shafts: the central (I in illustration 1.3) and hollow outer (A), i.e. the central shaft is hollow inside. Driven gears are on three shafts (1-3). The combined clutch is driven hydromechanically, with automatic control by commands from the electronic transmission control unit.
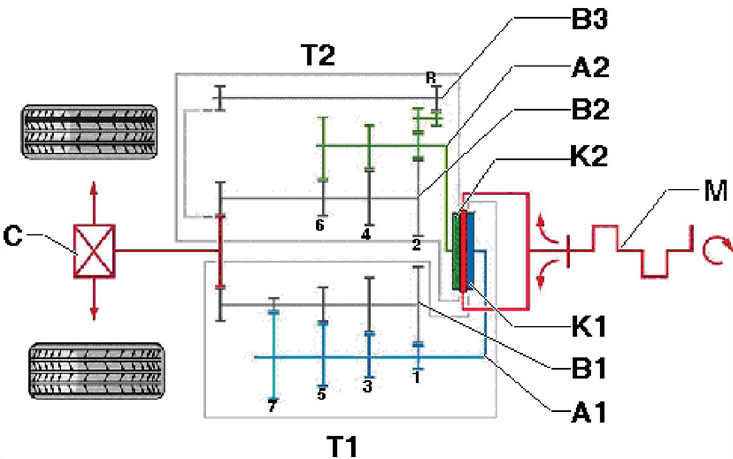
1.2 Torque transmission scheme
A1 Input shaft No. 1
A2 Input shaft #2
В1-ВЗ Output shaft No. 1 - No. 3
C Main gear
K1 Clutch No. 1
K2 Clutch #2
M Engine
T1 Part of the DSG with odd gears
T2 DSG part with even gears and reverse gear
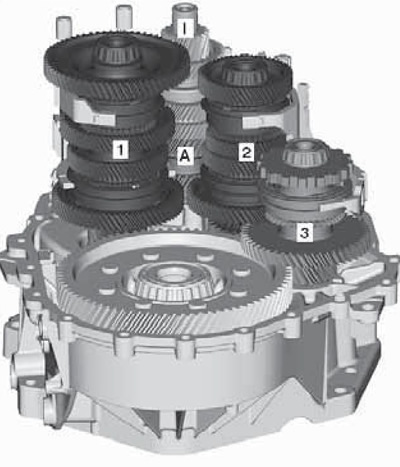

1.3 DSG shafts "OAM"
A External input shaft
I Internal input shaft
1-3 Output shaft 1-3
Maintaining the correct level of fluids in the transmission is essential to the proper operation of the transmission. In DSG "OAM" There are two working fluid circuits, each using different working fluids. One circuit (And in illustration 1.4) - with transmission oil, and the other (IN) - with hydraulic control unit working fluid "Mechatronic". Both of these fluids are filled for the life of the transmission and are not checked or topped up. The correct level is reached when changing the gear oil. The mode of periodic inclusion of the hydraulic pump is applied "V40T" according to the needs of the control system. In this mode, the hydraulic pump is turned on only when the pressure in the control unit "Mechatronic" falls below a certain value. Thus, for the functioning of the block "Mechatronic" the pump does not need to be constantly running.
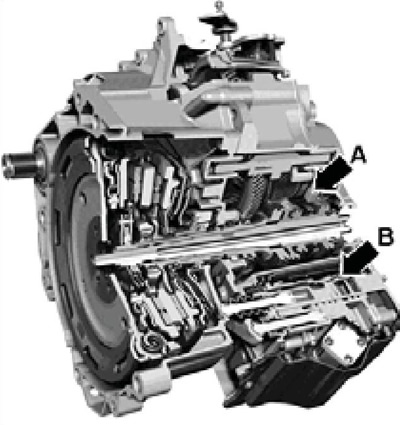
1.4 DSG fluid circuits "OAM"
The main details of the DSG are shown in illustration 1.5.
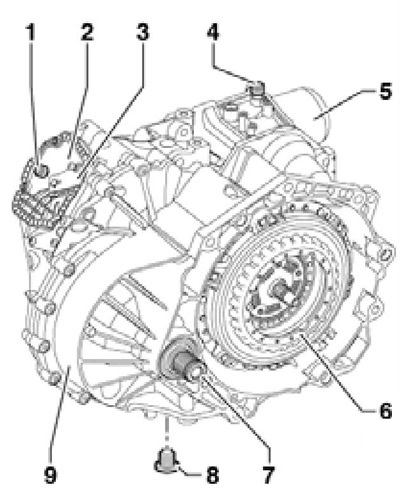
1.5 Basic parts of the DSG "0AM"
1 DSG breather cap
2 Transmission oil filling cap
3 Selector lever
4 Block breather cap 5
5 Control unit "Mechatronic"
6 Double clutch
7 Splined shaft (until 11.2008) or flanged shaft (since 11.2008)
8 Drain plug, 30 Nm
9 DSG "OAM"
Description of transmission control and its modes is given in Chapter "Controls and methods of operation". Gear shifting is carried out by means of hydraulic activation, with electronic control.
To repair the transmission, a lot of special tools are required, so the disassembly and assembly of the transmission and its components should be entrusted to service stations with the appropriate equipment.
