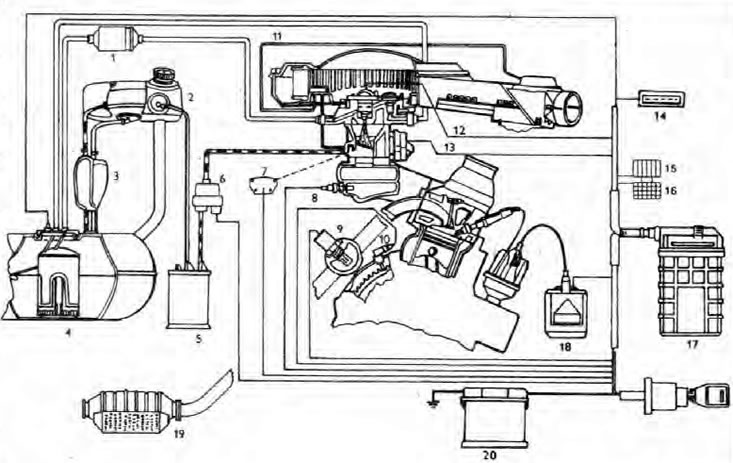
Diagram of the Bosch Mopo-Motronic engine management system
1. Fuel filter; 2. Filler neck of the fuel tank; 3. Leveling tank; 4. Fuel tank with electric pump; 5. Active carbon filter; 6. Solenoid valve for recirculation of fuel vapors; 7. Throttle position sensor; 8. Coolant temperature sensor; 9. Lambda sensor; 10. Position and crankshaft speed sensor; 11. Intake air temperature controller; 12. Fuel (nozzle; 13. Idler code frequency regulator; 14. Diagnostic socket; 15. Fuse; 16. Fuel pump relay; 17. Electronic control unit; 18. Ignition coil with amplifier; 19. Catalytic converter; 20. Battery.
Bosch Mono-Motronic system - engine management system that controls fuel injection and ignition (see illustration). This Section describes only the components of the fuel injection system - information about the components of the ignition system see Section 5.
The fuel injection system includes a fuel tank, an electric fuel priming pump, a fuel filter, fuel supply and return lines, a throttle body with an integrated electric fuel injector, and an electronic control device (ECU) together with associated sensors, actuators and wiring,
The fuel priming pump delivers fuel through the filter to the throttle body, at a pressure slightly higher than required - the fuel pressure regulator is built into the throttle body and maintains the fuel pressure in the nozzle at a constant level, returning excess fuel to the tank through the return pipe. Due to the constant circulation of the fuel, its temperature is reduced and evaporation is prevented. The fuel injector is opened and closed by an electronic control device (ECU), which calculates the injection timing and duration based on information about the engine speed, throttle position and degree of opening, intake air temperature, coolant temperature, driving speed and the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas received from sensors installed on the engine.
Inlet air enters the engine through the air filter, which contains a replaceable paper filter element. The inlet air temperature is controlled by a vacuum controlled valve in the air filter inlet that mixes cold air with hot air from the exhaust manifold heater. Vacuum supplied to the valve. regulated by a temperature sensor installed in the air filter.
The temperature of the air entering the throttle body is measured by a sensor mounted directly above the nozzle. This information is used by the ECU to accurately dose fuel based on temperature. Idle speed control is achieved partly by an electrically operated throttle valve mounted on the side of the throttle body and partly by an ignition system that corrects the idle speed by varying the ignition timing. As a result, manual idle speed adjustment is not required.
The oxygen content in the exhaust gas is constantly monitored by the ECU via a lambda sensor which is installed in the exhaust pipe of the ECU and then uses this information. to change the injection timing and duration, thereby maintaining the optimum air-fuel ratio - as a result, manual adjustment of the CO content in idling is not required. All models considered in this Section are equipped with a catalytic converter.
In addition, the ECU controls the operation of the carbon filter of the fuel vapor absorption system.
It should also be noted that troubleshooting the Bosch Mono-Motronic system is only possible with special test equipment. Therefore, in case of problems with the system, please contact your dealer. Once the damage has been determined, the corresponding component can be replaced (removal/installation sequences are described in subsequent Chapters).
