Car engine overhaul Skoda Favorit
Engine Removal and Overhaul Procedures — General Description
This Part of Section 2 describes the procedures for removing the engine/transmission assembly from the vehicle and the basic procedures for overhauling the cylinder head, cylinder block/crankcase, and all internal...
This Part of Section 2 describes the procedures for removing the engine/transmission assembly from the vehicle and the basic procedures for overhauling the cylinder head, cylinder block/crankcase, and all internal...
Engine Overhaul — General Description
It is not always easy to determine if an engine needs to be overhauled. it depends on many factors. High mileage does not necessarily mean a rebuild is necessary, and vice versa, low mileage does not eliminate the need...
It is not always easy to determine if an engine needs to be overhauled. it depends on many factors. High mileage does not necessarily mean a rebuild is necessary, and vice versa, low mileage does not eliminate the need...
Engine and Transmission Removal — Methods and Precautions
If the engine needs to be removed for overhaul, there are a few preliminary steps to take. Choosing a place to work is extremely important. You will need sufficient working space as well as a garage where you can leave...
If the engine needs to be removed for overhaul, there are a few preliminary steps to take. Choosing a place to work is extremely important. You will need sufficient working space as well as a garage where you can leave...
Engine and transmission — removal and installation
Removing Note: The engine can only be removed from the vehicle together with the transmission. after which they can be divided. The engine/transmission block is lowered from the engine compartment to the floor. 1. Park...
Removing Note: The engine can only be removed from the vehicle together with the transmission. after which they can be divided. The engine/transmission block is lowered from the engine compartment to the floor. 1. Park...
Engine disassembly sequence
1. It will be much easier to work if you install the engine on a special portable bed. Before installing the engine on the frame, remove the flywheel so that the frame bolts can be screwed into the cylinder block. 2. If...
1. It will be much easier to work if you install the engine on a special portable bed. Before installing the engine on the frame, remove the flywheel so that the frame bolts can be screwed into the cylinder block. 2. If...
Cylinder head — disassembly
Note: Given that. If special tools are required to remove and inspect the head, it is recommended that you purchase a new or remanufactured component from an engine remanufacturer. In the end, this can come out cheaper...
Note: Given that. If special tools are required to remove and inspect the head, it is recommended that you purchase a new or remanufactured component from an engine remanufacturer. In the end, this can come out cheaper...
Cylinder head and valves — cleaning and inspection
1. A complete cleaning of the cylinder head and valve components followed by a detailed inspection will allow you to determine what procedures need to be performed during an engine overhaul. Note: If the engine has been...
1. A complete cleaning of the cylinder head and valve components followed by a detailed inspection will allow you to determine what procedures need to be performed during an engine overhaul. Note: If the engine has been...
Cylinder Head — Assembly
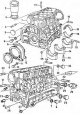
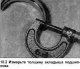
Pic. 2B.2. Location of valve components in the cylinder head 1. Cylinder head; 2. valve seat; 3. Valve; 4. Valve guide; 5. External spring support; 6. Internal spring support; 7. Valve guide valve stem cap; 8. Spring...
Pic. 2B.2. Location of valve components in the cylinder head 1. Cylinder head; 2. valve seat; 3. Valve; 4. Valve guide; 5. External spring support; 6. Internal spring support; 7. Valve guide valve stem cap; 8. Spring...
Camshaft and pushers — removal, inspection and installation
Removing 1. Remove the valve train as described in Chapter 5 of Section 2A . 2. Remove the push rods one by one and fold them in the correct order by pushing them into the cardboard holder. 3. Remove the four nuts...
Removing 1. Remove the valve train as described in Chapter 5 of Section 2A . 2. Remove the push rods one by one and fold them in the correct order by pushing them into the cardboard holder. 3. Remove the four nuts...
Piston and connecting rod assemblies — removal
1. Remove the cylinder head, sump and oil pump gears as described in Chapters 6 , 9 and 10 from Section 2A . Make sure the cylinder liners are securely in place. 2. Before removing the cranks, notice the two numbers...
1. Remove the cylinder head, sump and oil pump gears as described in Chapters 6 , 9 and 10 from Section 2A . Make sure the cylinder liners are securely in place. 2. Before removing the cranks, notice the two numbers...
Crankshaft, camshaft and related components
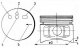
Pic. 2B.3. Crankshaft, camshaft and related components 1. Crankshaft; 2. Segment key; 3. Flywheel; 4. Flywheel ring gear; 5. Locating pin; 6. Flywheel mounting bolt; 7. Blocking plate; 8. Thrust washers of the...
Pic. 2B.3. Crankshaft, camshaft and related components 1. Crankshaft; 2. Segment key; 3. Flywheel; 4. Flywheel ring gear; 5. Locating pin; 6. Flywheel mounting bolt; 7. Blocking plate; 8. Thrust washers of the...
Crankshaft — removal
1. Remove the cylinder head, drive chain and sprockets as described in Chapters 6 and 7 from Section 2A . Make sure the cylinder liners are securely in place. 2. Release the connecting rod caps from the crankshaft and,...
1. Remove the cylinder head, drive chain and sprockets as described in Chapters 6 and 7 from Section 2A . Make sure the cylinder liners are securely in place. 2. Release the connecting rod caps from the crankshaft and,...
Cylinder block / crankcase — cleaning and inspection
Cleaning 1. For a complete cleaning, remove the liners (see paragraph 19 below), lube port plugs, and all external components and electrical switches/sensors. 2. Clean the cylinder block and crankcase of gasket residue,...
Cleaning 1. For a complete cleaning, remove the liners (see paragraph 19 below), lube port plugs, and all external components and electrical switches/sensors. 2. Clean the cylinder block and crankcase of gasket residue,...
Piston/Connecting Rod Assemblies — Disassembly, Inspection and Assembly
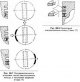
Pic. 2B.4. Piston head marking and diameter measuring point 1. Manufacturer's number 2. Manufacturer's mark 3. Piston size class (diameter) 4. Production date 5. Arrow (points towards the front of the cylinder block)...
Pic. 2B.4. Piston head marking and diameter measuring point 1. Manufacturer's number 2. Manufacturer's mark 3. Piston size class (diameter) 4. Production date 5. Arrow (points towards the front of the cylinder block)...
Crankshaft — inspection
1. Clean the crankshaft and dry it with compressed air. Make sure the oil holes are not clogged. 2. Check the main and connecting rod journals for uneven wear, scratches, corrosion, and cracks. 3. Run a copper coin...
1. Clean the crankshaft and dry it with compressed air. Make sure the oil holes are not clogged. 2. Check the main and connecting rod journals for uneven wear, scratches, corrosion, and cracks. 3. Run a copper coin...
Main and connecting rod bearings — inspection
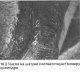
Pic. 2B.6. Typical earbud damage A. Scratched by foreign particles - grains are visible, immersed in the working spo of the liner IN. Lack of oil - the top layer is erased From the inserts are incorrectly positioned...
Pic. 2B.6. Typical earbud damage A. Scratched by foreign particles - grains are visible, immersed in the working spo of the liner IN. Lack of oil - the top layer is erased From the inserts are incorrectly positioned...
Engine Assembly Sequence
1. Before starting assembly, make sure that all necessary new parts are available and all tools are ready. Read the description of all procedures to familiarize yourself with the work. In addition to conventional tools...
1. Before starting assembly, make sure that all necessary new parts are available and all tools are ready. Read the description of all procedures to familiarize yourself with the work. In addition to conventional tools...
Piston rings — installation
1. Before installing new piston rings, check the cut gaps and the gaps between the ring and the groove wall as described in Chapter 13 . 2. When measuring new rings, place all piston/rod sets according to their location...
1. Before installing new piston rings, check the cut gaps and the gaps between the ring and the groove wall as described in Chapter 13 . 2. When measuring new rings, place all piston/rod sets according to their location...
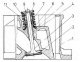
Crankshaft — setting and checking the operating clearance of the main bearing
Earbud selection 1. To select the required main bearings, you will first need to determine the size group of the crankshaft main journals. To do this, measure the diameters of the main journals and, based on the...
Earbud selection 1. To select the required main bearings, you will first need to determine the size group of the crankshaft main journals. To do this, measure the diameters of the main journals and, based on the...
Piston / connecting rod assemblies Installing and checking the operating clearance of the connecting rod bearing
Earbud selection 1. To select the required connecting rod bearings, you will first need to determine the size group of the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft. To do this, measure the diameters of the connecting...
Earbud selection 1. To select the required connecting rod bearings, you will first need to determine the size group of the connecting rod journals of the crankshaft. To do this, measure the diameters of the connecting...
Engine — start after overhaul
1. Check engine oil and coolant levels again. Be sure to connect all wires and hoses and do not leave any tools or rags in the engine compartment. 2. Remove the spark plugs, turn off the ignition system by connecting...
1. Check engine oil and coolant levels again. Be sure to connect all wires and hoses and do not leave any tools or rags in the engine compartment. 2. Remove the spark plugs, turn off the ignition system by connecting...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Link to this section in various formats
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- Engine in car
- Engine overhaul
- Cooling and heating
- Fuel and exhaust system
- Fuel injection system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis (running gear)
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body and interior
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (salon)
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to guide
- User manual
- Maintenance (petrol)
- Maintenance (diesel)
- Power unit
- Petrol engine 1.3 l
- Petrol engine 1.6 l
- Diesel engine
- Engine overhaul
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (carburetor)
- Central injection (SPFI)
- Multipoint injection (MPFI)
- Diesel power system
- Decreased toxicity
- Engine electrics
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis (running gear)
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body and interior
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (salon)
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Headlights and lighting
- Electrical circuits