Radiator of the cooling system
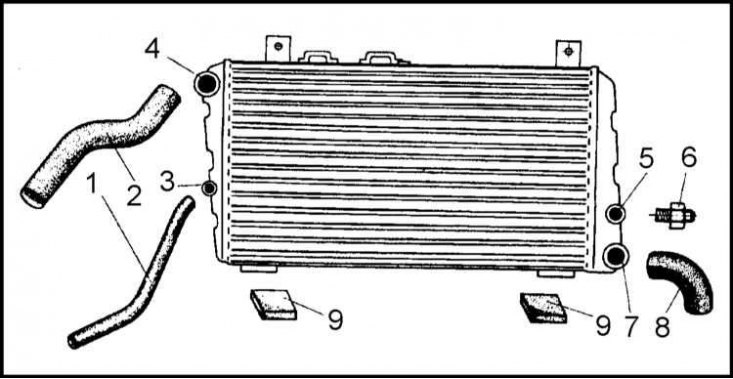
1 - Hose for supplying coolant from the engine; 2 - Hose for supplying coolant from the expansion tank; 3 - Pipe for supplying coolant from the thermostat housing; 4 - Pipe for supplying coolant from the expansion tank; 5 - Hole for the installation of a temperature-sensitive sensor-switch; 6 - Temperature-sensitive sensor-switch; 7 - Coolant outlet pipe; 8 - Coolant outlet hose; 9 - Rubber cushion supports
Radiator of the cooling system - general information
Models 1.3 l
1. In the engine cooling system of the car models under consideration, a tubular-type radiator with a horizontal coolant flow, manufactured under license from the French company Sofica, is installed. The general view of the radiator is shown in the illustration.
2. The radiator heat exchanger is a set of horizontal aluminum tubes connected at both ends to plastic side tanks. The joints are made by pressing, and the joints are sealed with rubber gaskets, planted on a special paste.
3. In the lower part of the right side tank there is a branch pipe for draining the coolant from the radiator, and above it there is a hole for fitting a temperature-sensitive sensor-switch.
4. In the upper part of the left side tank there is a coolant supply pipe, under it there is a pipe connecting the radiator to the expansion tank.
5. The bases of both side tanks through rubber cushions, the radiator rests on the transverse beam of the front of the car.
6. The upper edge of the radiator is attached to the upper transverse beam of the front end with two M6x12 bolts.
7. Due to the materials used, the radiator has a small mass and has greater external and internal corrosion resistance compared to traditional type radiators. At the factory, all radiators are mandatory tested for tightness, for which compressed air is supplied inside the heat exchanger, the pressure of which exceeds the operating values.
1.6L models without air conditioning
On models without K / V, equipped with a 1.6 liter engine, an oversized Autopal radiator is used (285x590). Both pipes are on the left side of the radiator, the liquid moves in a horizontal direction.
Diesel models without K/V and petrol models 1.6 l with K/V
1. These models use a radiator manufactured by AKG type ML3 with dimensions of 322x590 and oval tubes. The radiator is two-row, with a horizontal fluid flow.
2. The radiator mounting scheme has been slightly changed: lugs are provided in the lower part, on which rubber cushions are put on. Then the radiator is filled into the body openings. Two plastic clips with M6 bolts are provided on top.
Removing
Note. If the radiator is being removed to locate the source of the leak, remember that minor leaks can be repaired in situ using a special radiator sealant.
Disconnect the negative cable from the battery, then empty the cooling system.
Petrol models
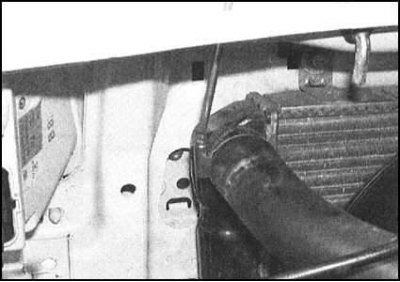
1. Release fastening collars and...

... Disconnect the upper and lower hoses from the radiator. On 1.3L models, also disconnect the expansion tank hose.
 |  |
2. Disconnect sockets of electroconducting of a driving motor and the gauge switch of the fan of system of cooling. Release the electrical wiring from the clips on the radiator case and fan shroud.
3. Turn out bolts of fastening of a radiator to the top transverse beam of a front end of the car (the latch of the hood latch is mounted in this beam).
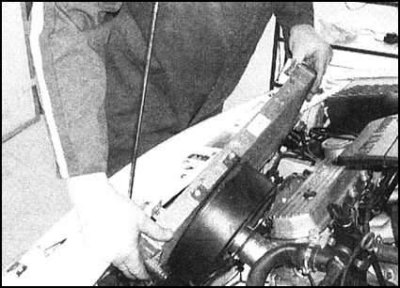
4. Having removed from the lower supports, remove the radiator from the engine compartment...
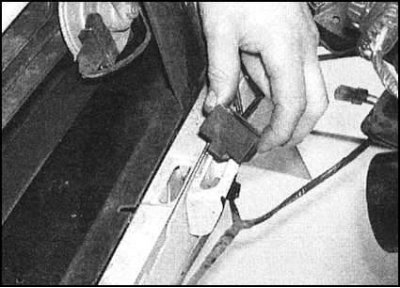
...be careful not to lose the rubber pads on the lower supports.
Note. On some models, in order to provide sufficient working space, it will be necessary to unbolt and remove the reinforcing rod connecting the upper cross member of the front end to the front skirt.
Diesel models
1. Release a collar and disconnect the top hose from a radiator.
2. Remove the mounting bolt on your lower hose coolant tube bracket. Release a collar, disconnect a tube from a hose of a casing of the thermostat and take it from an impellent compartment.
3. Remove the cooling fan assembly (see Section Check of serviceability of functioning, removal, installation, dismantling and assembly of the fan of the cooling system).
4. Disconnect the electrical wiring from the sensor-switch of the cooling system fan screwed into the radiator.
5. On models equipped with power steering, unbolt the hydraulic fluid reservoir from the cross member and move it away from the radiator. Be careful not to tilt the reservoir excessively to avoid splashing liquid.
6. Turn out bolts of fastening of a radiator to the top transverse beam of a front end of the car (with hood latch).
7. Remove the radiator from the lower supports and remove it from the engine compartment. Immediately remove the rubber pads of the lower supports.
Status check
1. If the reason for the removal of the radiator was the suspicion of a violation of the patency of its heat exchanger, it should be back-flushed. Soft brush (do not cut your fingers on the edges of the plates) clean the gaps between the radiator heat exchanger plates. If you have access to a compressed air source, blow out the gaps (don't forget to wear safety glasses).
Attention! Remember that the fragile plates of the radiator heat exchanger can easily be damaged by careless handling!
2. If necessary, at the service station, you can make "flowing" check the radiator for blockages of internal channels.
3. Repair of a radiator that has lost its tightness should be carried out only in a specialized workshop. Trying to fix the situation with a soldering iron will only damage the plastic components.
4. In an extreme situation, minor coolant leaks from the radiator can be stopped with a special sealant without removing the radiator from the car (in situ). Follow the instructions for applying the sealant.
5. Before sending the radiator to a repair shop, remove the fan sensor-switch from it.
6. Check up a condition of rubber pillows of support of a radiator. Replace if necessary.
Installation
Installation is carried out in the reverse order of dismantling. Pay special attention to the following points:
- a) Check for correct engagement of the radiator in the lower support assemblies. Tighten the fixing bolts firmly.
- b) Track correctness of connection and reliability of fastening by collars of all hoses.
- c) In conclusion, do not forget to refuel the cooling system.
