Cylinder block with the main components of the crankshaft
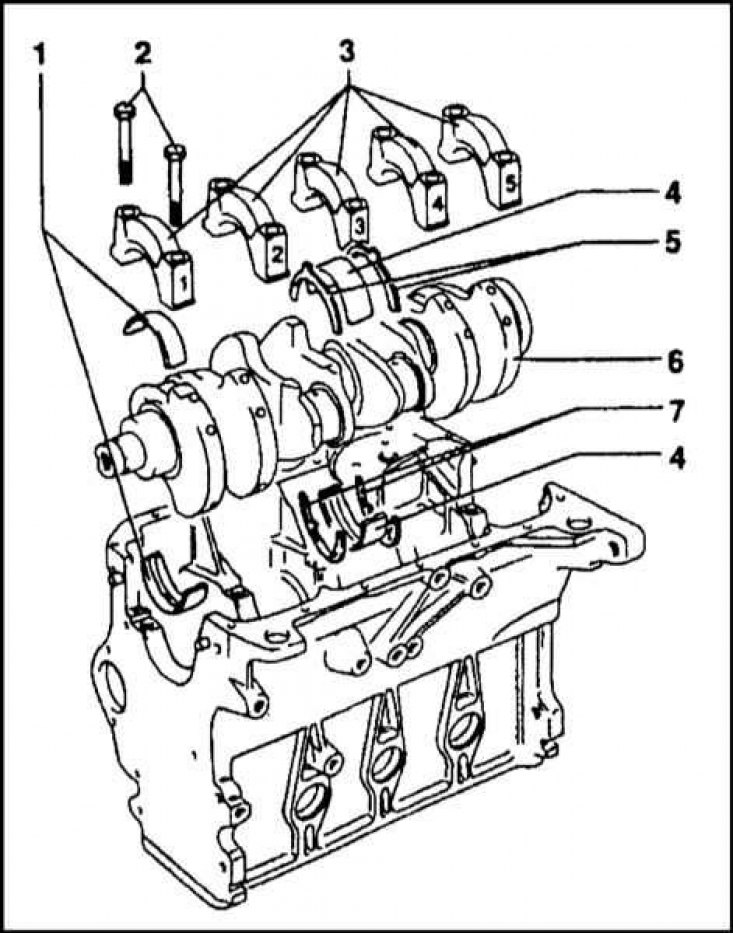
1 - Insert of the first main bearing; 2 - Bolts of fastening of a cover of the radical bearing; 3 - Main bearing caps; 4 - Liners of the third (stubborn) main bearing; 5 - Lower thrust half rings; 6 - Crankshaft; 7 - Lower thrust half rings
Cylinder block with crankshaft installation components
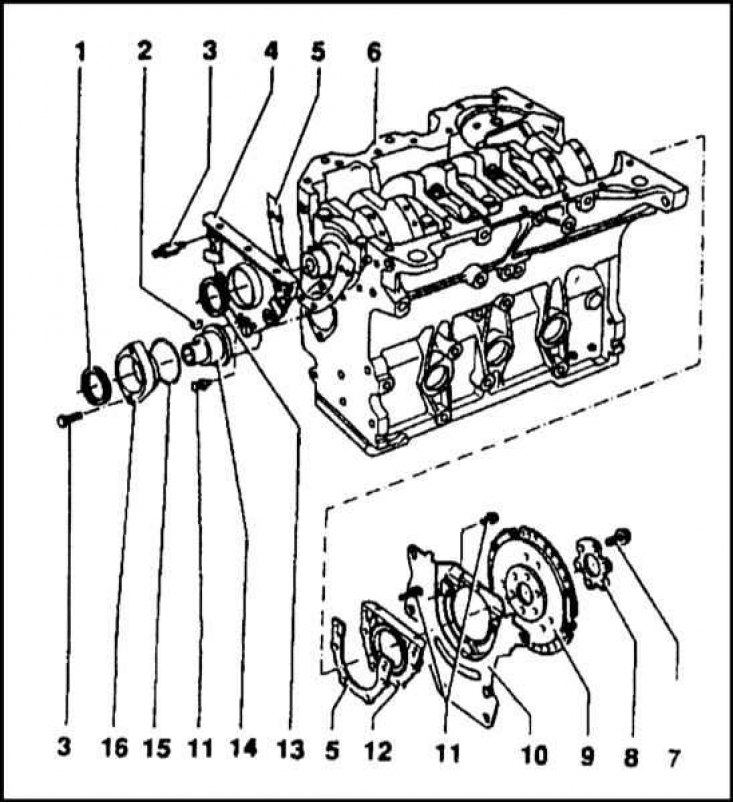
1 - Oil seal; 2 - Segment key; 3 - Mounting pin; 4 - Front cover; 5 - Sealing gasket; 6 - Cylinder block; 7 - Bolt; 8 - Flange; 9 - Flywheel; 10 - Back cover; 11 - Bolt; 12 - The holder of the rear oil seal; 13 - Oil seal; 14 - Intermediate shaft; 15 - O-ring; 16 - Gland holder
Connecting rod and piston assembly
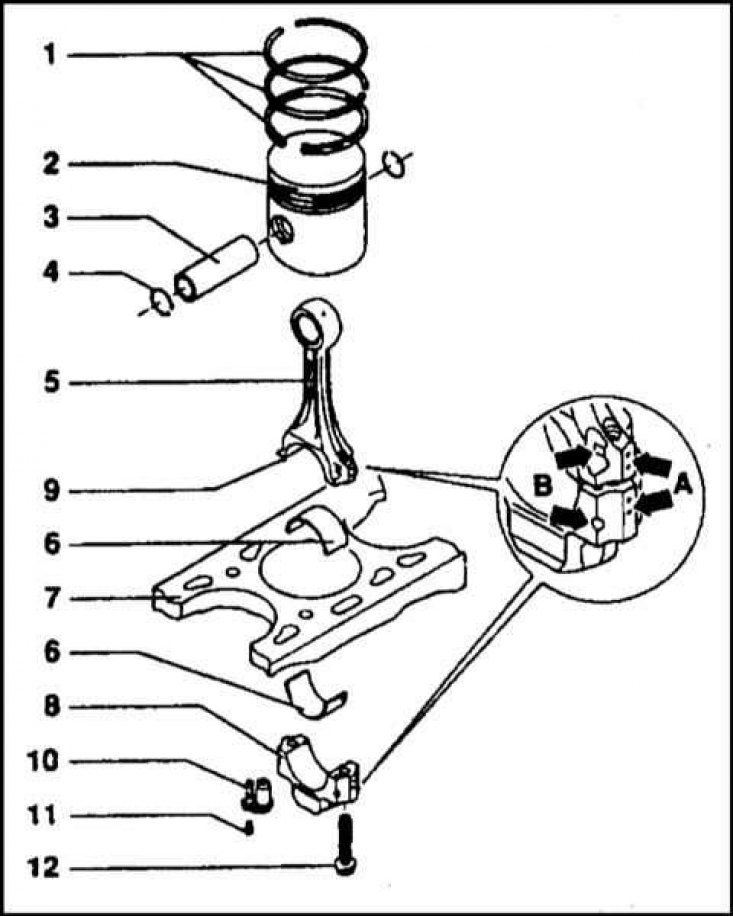
1 - Piston rings; 2 - Piston; 3 - Piston pin; 4 - Retaining rings; 5 - Connecting rod; 6 - Connecting rod bearing shells; 7 - Cylinder block; 8 - Cover of the lower head of the connecting rod; 9 - Locating pin; 10 - Oil jet; 11 - Bolt; 12 - Bolt
Cylinder head with valve train and timing components
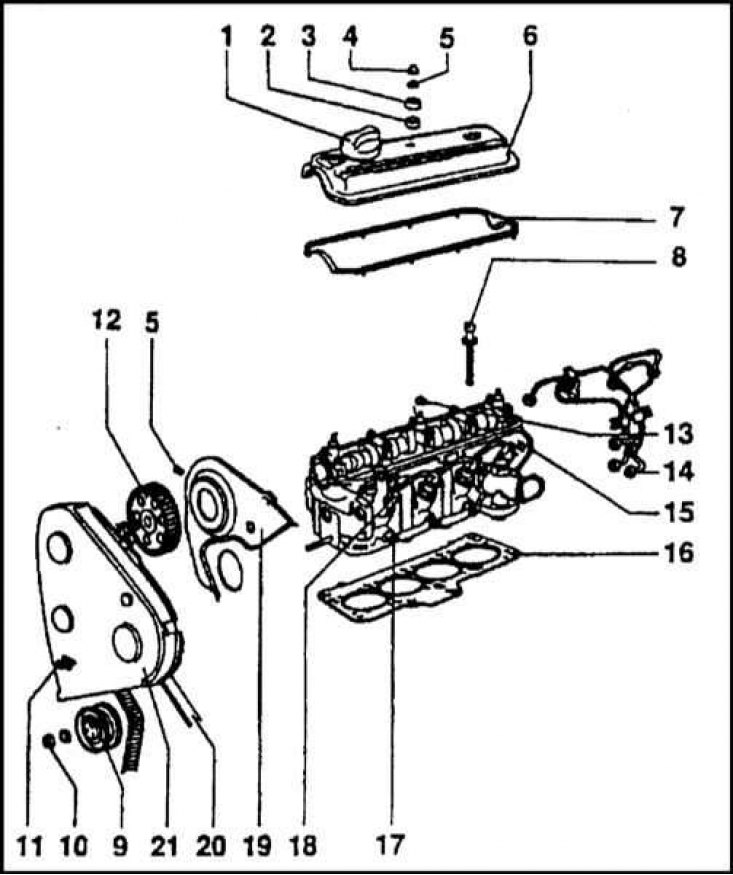
1 - Oil filler cap; 2 - Seal; 3 - Washer; 4 - Nut; 5 - Washer; 6 - Cylinder head cover; 7 - Cover gasket; 8 - Head bolt; 9 - Tension roller; 10 - Nut; 11 - Plank; 12 - Camshaft gear; 13 - Lower seal of the cylinder head stud; 14 - High pressure pipelines; 15 - Cylinder head; 16 - Sealing head gasket; 17 - Glow plug; 18 - Fuel injection nozzle; 19 - Cover; 20 - Toothed timing belt; 21 - Toothed belt guard
Camshaft and valve train installation components
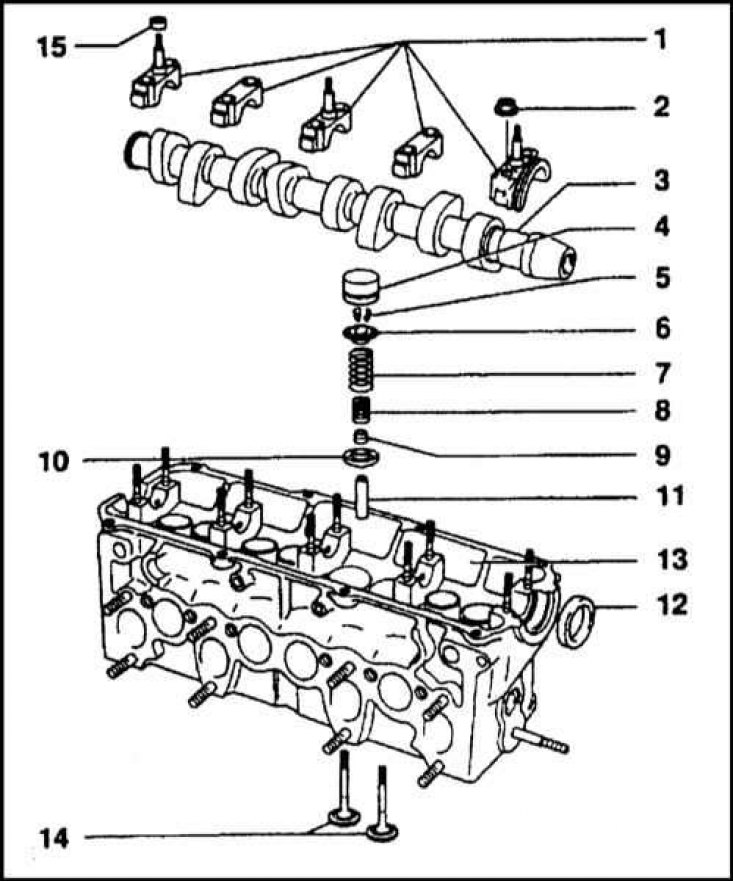
1 - Camshaft bearing caps; 2 - Nut; 3 - Camshaft; 4 - Hydraulic pusher; 5 - Crackers of a split lock; 6 - Plate of valve springs; 7 - External valve spring; 8 - Internal valve spring; 9 - Oil deflector cap; 10 - Washer; 11 - Guide sleeve; 12 - Oil seal; 13 - Cylinder head; 14 - Valves; 15 - Seal
Side view of the cylinder head
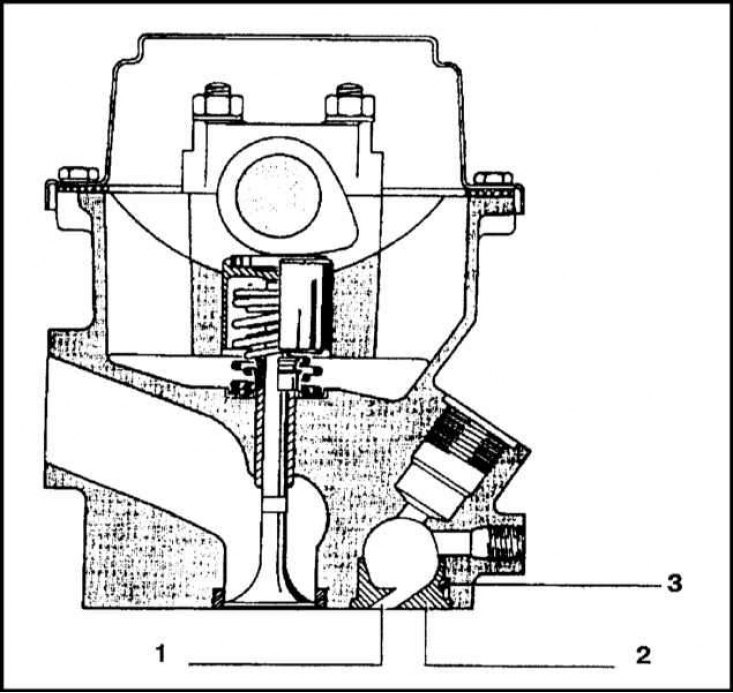
1 - Channel of the vortex chamber; 2 - Vortex chamber; 3 - Pin for fixing the position of the vortex chamber
Water pump
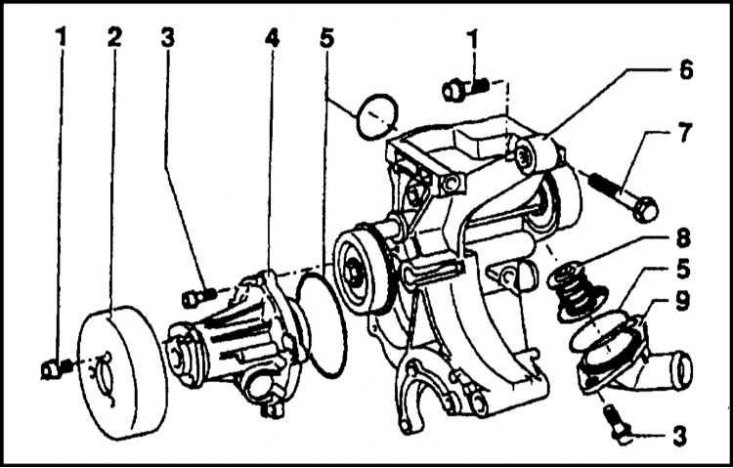
1 - Bolt; 2 - Pulley; 3 - Bolt; 4 - Water pump; 5 - O-ring; 6 - Bracket; 7 - Adjusting bolt; 8 - Thermostat; 9 - Thermostat housing
Cylinder block
Cylinder holes are machined in the cast-iron casting of the block and five main bearings of the crankshaft are formed. The general view and installation procedure of the cylinder block components are shown in the illustrations. The main bearing caps are attached to the block body with special M10 bolts. Third (average) the main bearing is thrust, perceives the arising axial loads and limits the longitudinal play of the shaft.
Crankshaft and intermediate shaft
The crankshaft is forged from steel. The journals of the main and connecting rod bearings are carefully polished. On the front trunnion of the shaft, there are places for landing the gear wheel of the timing belt and the sealing gland of the first main bearing. In addition to the crankshaft and distribution, the engine also has an intermediate shaft that transmits rotation from the crankshaft to the oil and vacuum pumps.
Connecting rod and piston group
Forged connecting rods have an I-section and a straight cut of the lower head. A bronze bushing is pressed into the top head. The lower head is cut in the middle and equipped with connecting rod bearing shells. The correct mutual position of the connecting rod cap and the connecting rod bearing shells is indicated by punched marks (A). When installed on the engine, the connecting rod must be turned with marks (IN) forward. The connecting rod bearing cap is bolted to the bottom head. In the process of overhaul, it is customary to replace the connecting rod bearing cap bolts.
The pistons are cast from aluminum alloy and have a flat bottom with a recess under the swirl chamber. When installing new connecting rod and piston assemblies, check the amount of protrusion of the pistons above the surface of the cylinder block in order to determine the required thickness of the gasket. For piston protrusions from 0.66 to 0.86 mm, a gasket with one mark is installed. With a protrusion of 0.87÷0.90 mm - with two, and, finally, with a protrusion of 0.91÷1.02 - with three. When selecting a gasket, the amount of protrusion of each of the pistons should be checked. The maximum result is taken as the starting point.
The piston pin has a floating fit. Before installing the pin, the piston should be heated to a temperature of 60°C. Finger fixation is carried out by means of two retaining rings.
Three grooves are made on the piston wall for the installation of piston rings. Two compression rings are installed in the upper grooves, and an oil scraper in the lower one. During the operation of the car, it is allowed to expand the gaps in the locks of the upper compression and oil scraper rings to a value of 1.2 mm, the lower compression - 0.6 mm. The maximum allowable lateral play of the compression rings is 0.25 mm, the oil scraper is 0.15 mm. When installed on the piston, the rings are turned by locks at an angle of 120°, so that one of the locks is not on the axis of the piston pin.
Cylinder head
A general view of the cylinder head with valve train components is shown in the illustration. The head is attached to the block with ten TORX head bolts. The tightening procedure for the bolts is the same as for the 1.6L petrol engine.
The head cover is seated on studs screwed into the camshaft bearings and fastened with three nuts.
The camshaft is laid in five bearings and is located directly above the valves. To drive the valves, tappets equipped with hydraulic valve clearance compensators are used.
Guide bushings and valve seats are pressed into the head and are among the replacement parts.
The valves are installed vertically and have an in-line arrangement. Each valve is equipped with two springs, which rest against the support washer with their lower ends, and against the plate with their upper ends. The plate of springs is fixed on the valve with crackers of a split lock.
The camshaft cam rests on the pusher not exactly in the center, which causes the valve to rotate during movement.
Valves are subjected to special treatment at the factory and do not need additional lapping. If defects are found, the valves (and their saddles) are to be replaced.
The steel camshaft rotates in five plain bearings that are not equipped with replaceable liners. Camshaft drive (and injection pump) carried out by a gear-belt transmission. The tension force of the toothed belt is adjusted automatically by the hydraulic tensioner. The belt is replaced after the engine is removed from the vehicle. When installing the belt, the marks on the crankshaft sprocket and cylinder block/flywheel and clutch dome, as well as the camshaft sprocket and belt cover, injection pump sprocket and mounting flange must be aligned.
The cast cylinder head cover is equipped with an oil filler neck equipped with a hermetically sealed screw plug. From below, the filler opening is closed by an oil deflector. To fasten the cover to the head, three nuts are used, closed from the outside with decorative rubber or plastic plugs.
Water pump
The water pump is different in design from those used on gasoline engines. The pump is mounted on a bracket to which the thermostat housing with outlet pipe is attached.
