The injection pump is driven by a timing belt and rotates twice as slowly as the crankshaft. Diesel fuel is sucked in by the pump from the tank and passed through the fuel filter. Further, it is fed under very high pressure through individual lines to the nozzles.
Injectors are spring-loaded mechanical valves that open when the pressure of the fuel supplied to them exceeds a certain predetermined value. When the valves are opened, fuel is injected through the nozzle nozzles into the vortex chambers (indirect injection system). Note that the design of the nozzles is such that as the pressure increases, the valves open in two stages, which allows for the most efficient combustion of the mixture.
The basic setting of the injection phases is determined by the position of the injection pump on its support bracket. Adjustment (delay or advance) phases with the engine running is produced by the pump itself mechanically, depending on the position of the gas pedal and engine speed.
The engine is stopped by means of a shut-off solenoid valve, which, when activated, shuts off the fuel supply to the high-pressure fuel pump. On most models, this valve is included in the anti-theft system circuit. Until the immobilizer is disabled, the engine cannot be started.
During a cold start, the engine idle speed is increased by means of an automatic idle speed increase device installed on the wall of the high-pressure fuel pump.
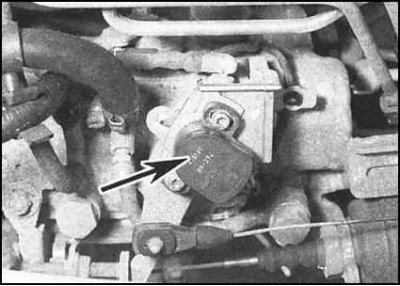
The engine is also equipped with a control unit that controls the operation of glow plugs and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). The unit is located next to the glow plug relay in the left rear corner of the engine compartment. Information about the current distance load is supplied to the control unit by a potentiometer attached to the throttle actuator lever. The injection start valve installed in the high-pressure fuel pump transmits information about the fuel supply phases to the control unit.
The control unit includes a unit for self-diagnostics of fuel injection pump failures. The diagnostic connector is located on the right under the instrument panel. Reading the information recorded in the memory of the block is possible only with the help of special equipment and should be carried out by car service specialists. A description of the procedures for removing / installing the pump in order to eliminate the causes of the identified malfunctions is given in the materials of the Chapter.
Precautionary measures
Warning! Diesel fuel is a highly flammable liquid. Special precautions must be observed when servicing power system components!
Do not smoke and do not approach the work area with an open flame source / unprotected carrier! Do not service power system components in rooms equipped with natural gas-fired, pilot flame-equipped heaters. Keep a charged fire extinguisher handy at all times.
Avoid getting fuel in eyes and on exposed skin. Wear protective gloves and goggles. Wash off accidental splashes with soap and water.
Remember that fuel vapors are no less, if not more, dangerous than liquid fuel itself. Perform all work in a well ventilated area.
Many of the procedures described in this chapter involve the need to disconnect fuel lines, inevitably leading to fuel spills. Try to prepare in advance all the necessary materials to collect spilled fuel.
Be aware that the trigger pressure of the nozzles is very high and if the jet from the nozzle hits exposed areas of the body, serious injury can result. The authors of this manual recommend that all pressure testing of the system be performed by a qualified service technician.
In no case do not allow diesel fuel to get on the hoses of the cooling path, immediately remove accidental splashes with a clean rag. Fuel-contaminated hoses must be replaced.
The power supply system of a diesel engine is particularly sensitive to various kinds of pollution. When servicing system components, try to keep the components clean and prevent dirt from getting inside the tract. Wipe the fittings thoroughly before connecting hoses. Store removed components in clean containers. Use only a lint-free cloth to wipe the parts. Avoid using compressed air to purge in situ power system components.
