Cylinder block and its internal components
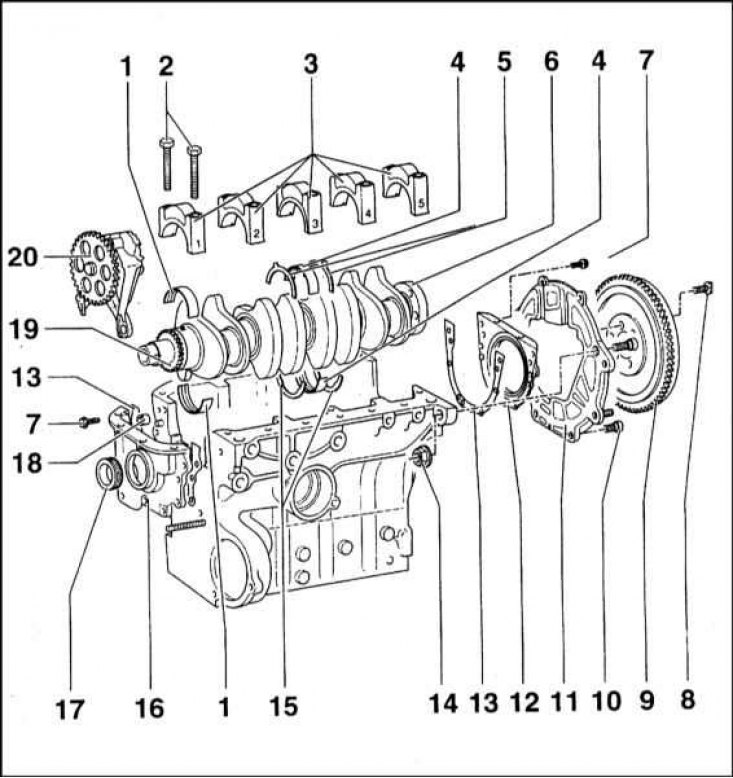
1 - Insert of the main bearing; 2 - Bolts of fastening of a cover of the radical bearing; 3 - Main bearing caps; 4 - Liners of the third (stubborn) main bearing; 5 - Lower thrust half rings; 6 - Flange for landing the flywheel; 7 - Flywheel mounting bolt; 8 - Flywheel mounting bolt; 9 - Flywheel; 10 - A bolt of fastening of a back cover; 11 - Back cover; 12 - The holder of an epiploon; 13 - Sealing gasket; 14 - Self-locking nut; 15 - Lower thrust half rings; 16 - Front cover; 17 - Front oil seal; 18 - Mounting sleeve; 19 - Oil pump drive gear; 20 - Oil pump
Connecting rod and piston assembly
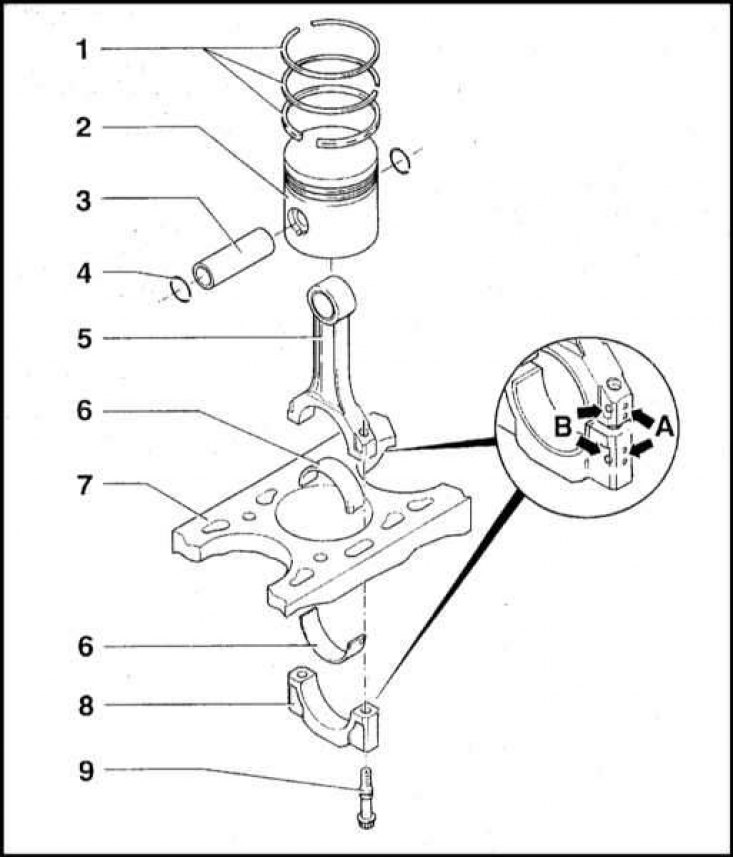
1 - Piston rings; 2 - Piston; 3 - Piston pin; 4 - Retaining ring; 5 - Connecting rod; 6 - Inserts; 7 - Cylinder block; 8 - Cover of the lower head of the connecting rod; 9 - Cover bolt
Cylinder head and valvetrain components
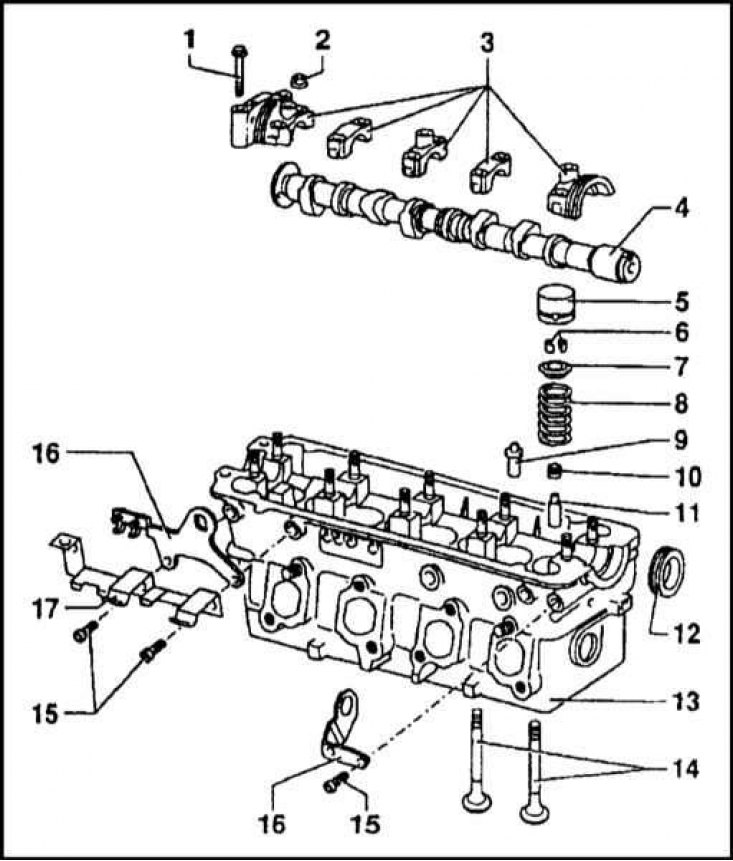
1 — Bolt of fastening of a cover of the first support of a camshaft; 2 - Nut of the mounting stud; 3 - Camshaft bearing caps; 4 - Camshaft; 5 - Hydraulic pusher; 6 - Crackers of a split lock; 7 - Valve spring plate; 8 - Valve spring; 9 - Guide sleeve (repair); 10 - Oil deflector cap; 11 - Guide sleeve; 12 - Oil seal; 13 - head casting; 14 - Valves; 15 - Bolts; 16 - Spring; 17 - Bracket BB wires
Scheme of functioning of the hydraulic pusher
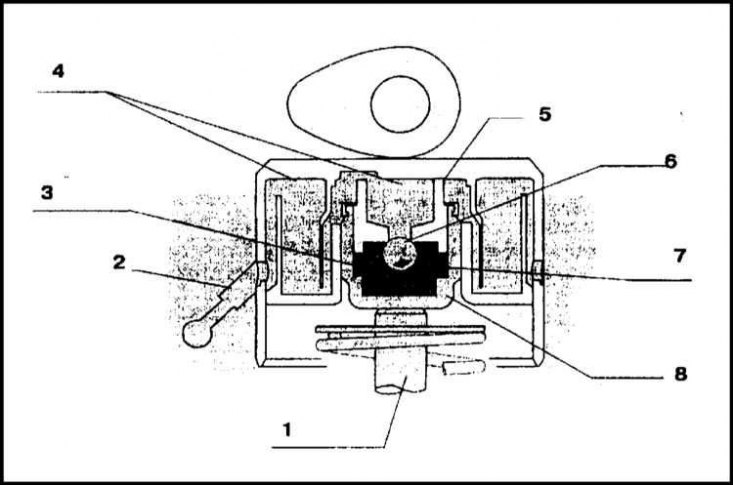
1 - Valve stem; 2 - Oil supply; 3 - Oil chamber; 4 - Low oil pressure; 5 - Piston; 6 - Ball valve; 7 - Spring; 8 - Plunger body
Timing drive scheme
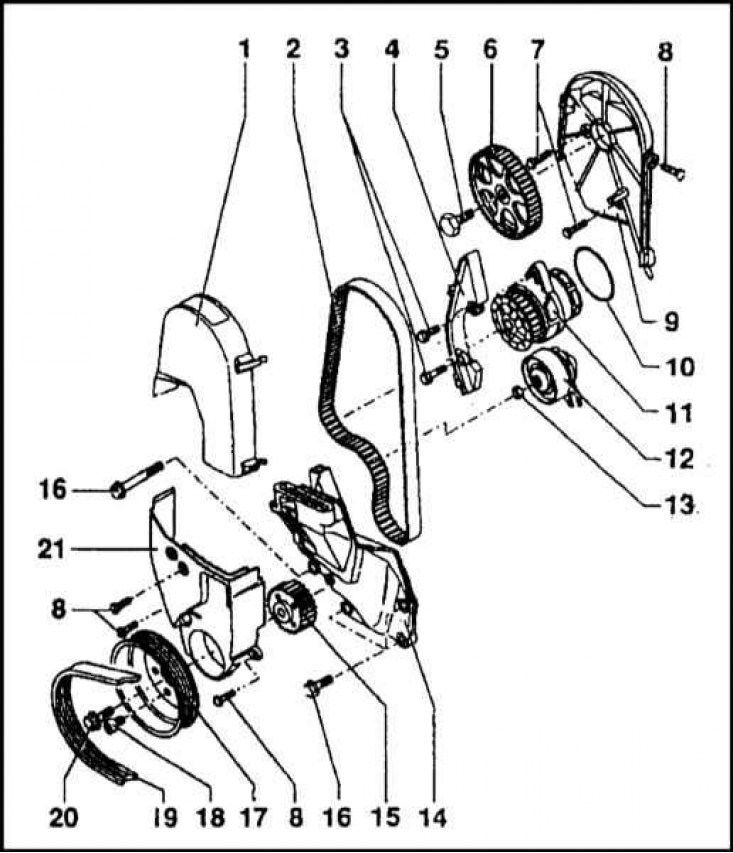
1 - Top cover; 2 - Toothed belt; 3 - Bolts; 4 - Belt guard at the location of the water pump; 5 - Bolt; 6 - Timing belt camshaft; 7 - Bolts; 8 - Bolts; 9 - Inner cover; 10 - O-ring; 11 - Water pump; 12 - Tension roller; 13 - Nut; 14 - Cover; 15 - Crankshaft gear; 16 - Bolt; 17 - Bolt; 19 - Multirib drive belt for auxiliary units; 20 - Bolt; 21 - Bottom cover
Cylinder block
The cylinder block is cast iron. The general view and installation procedure of the cylinder block components are shown in the accompanying illustration. Cylinders are machined directly in the body of the block. In the lower part of the block, five beds of crankshaft main bearings are made. Bearing caps are attached to the block with special M10x65 bolts. Washers under the bolt heads are not installed.
The axial play of the crankshaft is controlled by thrust half rings mounted on the third main bearing.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is forged from steel and consists of five main and four connecting rod journals. An oil pump drive gear is fixed on the front axle of the shaft and a groove is provided for installing a segment key for fitting the timing belt gear wheel. At the rear end of the shaft is equipped with a flange for the installation of a flywheel.
Connecting rod and piston group
Forged connecting rods have an I-section and a straight cut of the lower head. A bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head, which is then machined to the required diameter (17.6mm). The lower head is cut in the middle and then machined to a diameter of 50.6+0.01 (without inserts). The correct mutual position of the connecting rod cap and the connecting rod bearing shells is indicated by special marks. In addition, the number of the cylinder to which this connecting rod corresponds is also knocked out on the head. The connecting rod bearing cap is attached to the lower head with M8x1 TORX bolts. In the process of overhaul, it is customary to replace the connecting rod bearing cap bolts. The components of the connecting rod and piston assembly are shown in the illustration.
The pistons are cast from aluminum alloy and have a concave bottom, the cavity of which partly forms the volume of the combustion chamber. When installing, the piston should turn with a mark on the bottom in the direction of the timing drive. The floating piston pin is held in place by two circlips. When landing on the connecting rod, the piston is heated to 60°C, after which the piston pin is filled into it. Two compression rings and one oil scraper ring are installed on each of the pistons.
Cylinder head and gas distribution mechanism
In the cylinder head there are in-line valves. The layout of the valve mechanism components in the head is shown in the illustration.
The cylinder head is attached to the block with ten special M11x1.5 TORX bolts. The sealing head gasket has a metal edging of the holes for the cylinders, and is covered with a silicone sealing layer around the perimeter. The correct position of the gasket on the block is ensured by two dowel pins seated in the mating surface of the cylinder block.
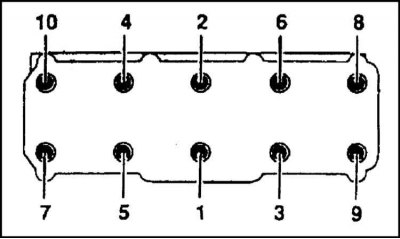
The order of a tightening of bolts of fastening of a head of cylinders is shown in an illustration.
The inlet and outlet channels are brought out on opposite sides of the head. Seats and valve guides are pressed into the body of the head, and camshaft bearings are also formed. The camshaft bearing caps are mounted in the head with M7 bolts. Oil seals are planted inside the housings of the extreme bearings.
The valves are driven directly from the camshaft through tappets equipped with hydraulic compensators. Hydraulic compensators provide backlash-free valve drive. The operation diagram of the hydraulic pusher is shown in the illustration.
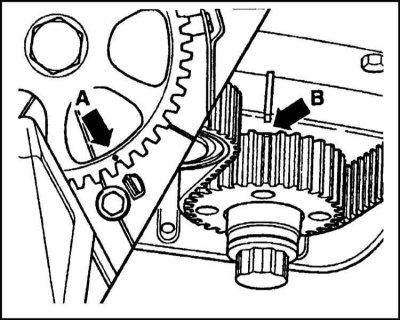
The timing gear is attached to the camshaft with an M14x1.5x47 bolt. The timing drive is carried out by a belt drive based on a toothed belt CR Power 137STD8-19. The tension force of the belt is provided by a tension roller, which at the same time increases the angle of coverage of the pulleys. When installing a toothed belt, it is necessary to achieve alignment of the alignment marks. After installing the belt, it is necessary to turn the crankshaft a few turns and again check the correct alignment of the marks.
Belt tension is adjusted automatically by a hydraulic tensioner. The timing drive diagram is shown in the illustration.
Water pump
A non-separable centrifugal water pump is attached to the cylinder block with two M8 bolts. The connection is sealed with a rubber sealing ring. The pump is driven by a toothed timing belt. In case of failure, the pump assembly is replaced.
Inlet pipeline and exhaust manifold
The intake piping is made of plastic and is divided into four passages that connect to the intake ports of the cylinder head. The joint is sealed with a sealing ring. Inside the intake manifold there is a flow meter and intake air temperature sensors, as well as an air thermostat. Outside, a tube of the fuel vapor recovery system is connected to the pipeline.
The exhaust manifold is studded and attached to the block with M8 nuts. A metal-reinforced sealing gasket is installed between the manifold and the head. When installing the exhaust manifold on the engine, the replacement of the gasket and fixing nuts is mandatory.
